Why SurferCloud UHost Is the Best Cloud Serve
December is always a busy month for developers, online ...







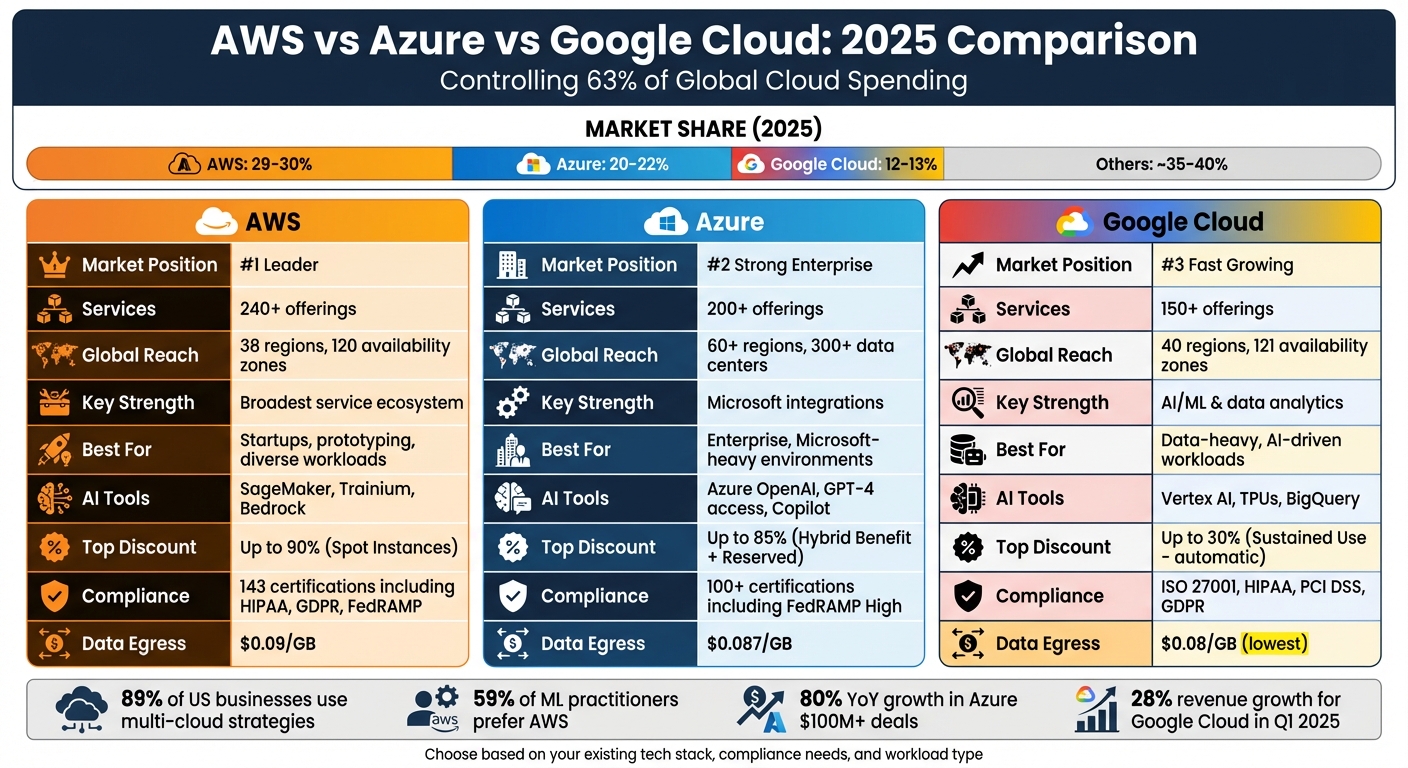
In 2025, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud remain the top cloud providers, controlling 63% of global cloud spending. Here's a quick breakdown:
Each platform suits different needs: AWS for its vast ecosystem, Azure for Microsoft-centric setups, and Google Cloud for AI and data-heavy workloads.
Quick Comparison:
| Feature | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Share | 29–30% | 20–22% | 12–13% |
| Key Strengths | Broad service range | Microsoft integrations | AI & analytics tools |
| Regions | 38 regions, 120 AZs | 60+ regions, 300+ data centers | 40 regions, 121 AZs |
| AI Tools | SageMaker, Trainium | Azure OpenAI, GPT-4 access | Vertex AI, TPUs |
| Pricing | Flexible, Spot savings up to 90% | Hybrid Benefit cuts costs by 85% | Sustained Use Discounts up to 30% |
Choosing the right platform depends on your goals, existing tools, and budget. Multi-cloud strategies are increasingly common, with 89% of businesses using multiple providers to combine their strengths.
AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud 2025: Market Share, Pricing & Key Features Comparison
By 2025, AWS continues to lead the cloud market, holding a 29–30% share, though this marks a slight dip from its 32–33% share in 2022. Microsoft Azure follows with a 20–22% share, while Google Cloud has shown notable growth, increasing its share from 9% to 13% by Q3 2025. The gap between the top three providers and the rest of the market remains stark, leading many to seek alternatives to AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud - Google Cloud is nearly four times larger than Alibaba Cloud, which holds a modest 4% share.
In the U.S., the cloud market has surged, growing by 28% in Q3 2025 and now outpacing the entire Asia-Pacific region. Revenue figures highlight this growth: AWS saw a 17% year-over-year increase in Q1 2025, Azure's Intelligent Cloud revenue jumped by 21% to $26.8 billion, and Google Cloud's revenue climbed 28% to $12.3 billion.
John Dinsdale, Chief Analyst at Synergy Research Group, remarked, "Amazon maintains a strong lead in the market, though Microsoft and Google once again had higher percentage growth numbers".
This competitive market landscape is supported by extensive global infrastructure, as detailed below.
When it comes to infrastructure, Azure operates the largest global network, with over 60 regions and more than 300 data centers. AWS follows with 38 geographic regions and 120 availability zones, while Google Cloud offers 40 regions and 121 availability zones. For U.S. enterprises, AWS’s North American coverage includes 31 availability zones across nine regions, along with 31 edge network locations, ensuring low-latency performance.
AWS designs its regions with three physically isolated zones, separated by up to 62 miles (100 km), to minimize risks from localized disasters while maintaining low-latency connectivity. Google Cloud takes a different approach, leveraging its "Global VPC" architecture, which allows a single network to span multiple regions seamlessly. Azure, meanwhile, focuses on broad geographic expansion and proximity to enterprise hubs, though some regions rely on a single data center.
To meet the demand for ultra-low latency, providers have introduced edge computing solutions. AWS offers Local Zones and Wavelength, Azure provides Edge Zones and Private 5G Core, and Google Cloud delivers Distributed Cloud Edge. These services achieve sub-10-millisecond latencies in major metro areas, with edge centers expected to grow from 250 to 1,200 by 2026.
Beyond infrastructure, compliance and data residency are critical for meeting security and regulatory requirements. All major cloud providers offer extensive compliance portfolios tailored to U.S. businesses. AWS leads with 143 security standards and certifications, including HIPAA, GDPR, and SOC 1/2/3, and provides specialized AWS GovCloud environments for federal use. Azure supports over 100 certifications, such as FedRAMP High, making it a strong choice for government and healthcare sectors. Google Cloud emphasizes security through automatic encryption and complies with key standards like ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR.
Across all providers, there are 486 FedRAMP-authorized cloud service offerings. The updated FedRAMP Agency Authorization process now follows Rev 5 guidelines, with the new "FedRAMP 20x" initiative piloting a cloud-native approach to streamline authorization. For businesses requiring strict data residency, AWS offers Outposts and Local Zones, Azure provides Arc and Stack HCI/Edge, and Google Cloud supports Anthos and Distributed Cloud Edge, enabling sensitive data to remain on-premises or within designated regions.
AWS boasts the most extensive service catalog, with over 240 offerings, including EC2 for virtual machines and Lambda for serverless computing. It also leverages custom chips to optimize machine learning workloads. For container orchestration, AWS provides ECS and EKS, catering to a wide range of deployment needs.
Microsoft Azure stands out in enterprise computing by integrating seamlessly with Microsoft’s core solutions. Azure Virtual Machines and Azure Functions work smoothly with existing Microsoft licenses, while AKS handles container management effortlessly. With Azure Arc and Azure Stack, businesses can achieve consistent hybrid cloud experiences across on-premises and cloud setups.
Google Cloud shines in container-native applications, thanks to Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) - the birthplace of Kubernetes. Its Compute Engine offers competitive virtual machines with per-second billing, while Cloud Functions supports serverless demands. Google Cloud also delivers about 10% better IaaS performance in benchmark tests. Moreover, its custom TPUs are tailored for superior price-performance in AI tasks.
In Q1 2025, Microsoft reported an 80% year-over-year growth in large Azure enterprise deals (valued at $100 million+), driven by integrations with Microsoft 365 and OpenAI services. Meanwhile, Clarifai’s platform team noted a 70% reduction in GPU costs and a 40% decrease in energy use on AWS by employing predictive scaling and carbon-aware scheduling.
All three providers now offer specialized AI accelerators - AWS's Trainium, Azure's Maia, and Google's TPUs - reflecting the 2025 trend toward hardware tailored for machine learning. For US businesses, the choice often depends on existing infrastructure: Azure is a natural fit for Microsoft-heavy environments, AWS offers the broadest ecosystem, and Google Cloud is ideal for Kubernetes-first strategies.
Next, let’s examine how these platforms compare in storage and database solutions.
Each cloud provider brings unique strengths to storage and database services:
| Service Category | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Object Storage | S3 | Blob Storage | Cloud Storage |
| Block Storage | EBS | Managed Disks | Persistent Disk |
| File Storage | EFS | Azure Files | Filestore |
| Relational DB | RDS, Aurora | SQL Database | Cloud SQL, Spanner |
| NoSQL DB | DynamoDB | Cosmos DB | Firestore, Bigtable |
| Data Warehouse | Redshift | Synapse Analytics | BigQuery |
AWS is well-suited for high-scale web and mobile applications, Azure caters to enterprises with hybrid needs, and Google Cloud is tailored for data-heavy, AI-driven workloads.
Now let’s explore how these platforms differentiate themselves in AI, machine learning, and analytics.
AI and analytics offerings play a pivotal role in shaping cloud platform preferences for US enterprises.
"Companies have largely finished cost optimization and are now focusing on new initiatives, which is expected to drive AWS spending on AI infrastructure."
– Andy Jassy, CEO, Amazon
"The number of $100 million-plus Azure deals increased more than 80% year over year."
– Satya Nadella, CEO, Microsoft
In 2025, the global machine learning market hit $113.10 billion, with the United States accounting for over $21 billion. For US businesses, Azure is the go-to for Microsoft integrations and hybrid governance, AWS leads in third-party integrations, and Google Cloud attracts those prioritizing advanced data analytics and TPU-powered solutions.
Here’s a closer look at how the pricing strategies of major cloud providers can directly influence your overall cloud spending.
All three providers primarily bill virtual machine (VM) instances per second, though AWS enforces a 60-second minimum for EC2 instances. For a standard 2vCPU, 8GB RAM instance, Google Cloud offers the lowest on-demand rate at $0.084/hour, compared to AWS and Azure, both at $0.096/hour. With 1-year reserved plans, the rates drop further: Google Cloud leads at $0.045/hour, followed by Azure at $0.048/hour, and AWS at $0.05/hour.
AWS offers Reserved Instances and Savings Plans, which can reduce costs by up to 72% compared to on-demand pricing. Azure provides a unique advantage for U.S. businesses with existing Microsoft licenses. Through the Azure Hybrid Benefit combined with Reserved Instances, organizations can save up to 85% on Windows Server and SQL Server workloads. Meanwhile, Google Cloud simplifies savings with Sustained Use Discounts, reducing costs by up to 30% for long-running instances - no commitments required.
For workloads that can handle interruptions, Spot and Preemptible instances are a game-changer, offering savings of up to 90% on AWS and 80% on Azure and Google Cloud. However, AWS Spot pricing tends to fluctuate significantly, with an average of 197 price changes per month, while Azure and Google Cloud experience far fewer adjustments, averaging less than one price change per month. Additionally, Arm-based instances (like AWS Graviton4) consistently provide better value, with Azure showing a 69% cost difference between x86 and Arm for Spot instances.
These pricing options set the stage for evaluating data transfer costs, which can also play a major role in your total cloud expenses.
Data egress fees can significantly affect the total cost of ownership for U.S. businesses transferring data between regions or out of the cloud. Google Cloud offers the most competitive outbound rate at $0.08 per GB, followed by Azure at $0.087 per GB, and AWS at $0.09 per GB. As of 2025, all three providers have eliminated inbound data transfer fees.
To remain competitive, each platform has reduced networking fees. AWS cut inter-region transfer costs by 10% and CloudFront egress charges by 15%. Similarly, Azure reduced inter-region traffic fees by 10%, while Google Cloud lowered outbound fees by 12% and completely eliminated CDN ingress charges. For content-heavy applications, using services like CloudFront (AWS) or Cloud CDN (Google Cloud) can help further minimize egress costs.
With these pricing details in mind, let’s now explore the cost management tools offered by each provider.
AWS Cost Explorer provides visual tools for tracking and analyzing spending, while AWS Budgets allows users to set custom alerts for specific spending thresholds. For detailed insights, the AWS Cost and Usage Report (CUR) offers granular data, and the AWS Compute Optimizer uses machine learning to suggest optimal resource configurations.
In the Azure ecosystem, Azure Cost Management + Billing serves as the central hub for monitoring expenses. Azure Advisor provides automated recommendations for rightsizing and identifying idle resources. In February 2025, Microsoft introduced "Copilot Nudges", an AI-powered feature within Azure Cost Management that proactively suggests deactivating idle resources or switching to more cost-effective plans.
Google Cloud focuses on simplicity with tools like Billing Reports and cost-table views. Its automatic Sustained Use Discounts provide savings without requiring manual intervention.
Cloud waste remains a common challenge, with companies typically losing up to 32% of their cloud budgets due to idle resources and lack of visibility. To tackle this, organizations are turning to advanced cost management tools. For example, in 2025, Drift used CloudZero's cost intelligence platform to save $4 million on their AWS expenses. Similarly, Ninjacat implemented real-time cost allocation and anomaly detection, cutting their cloud costs by 40%.
In April 2025, PlayPlay, a video platform, achieved monthly savings of $1,430 by using Cast AI to automate node rebalancing, replacing 13 Kubernetes nodes with more cost-efficient options - all without impacting service availability. For U.S. businesses, leveraging rightsizing tools can reduce compute expenses by up to 40%. Additionally, Azure’s enhanced cost allocation fields (updated in February 2025) allow for better financial accountability by categorizing expenses by department, project, or region.
Each cloud provider brings its own strengths to the table. Google Cloud stands out in AI, machine learning, and data analytics workloads. In fact, independent testing in 2025 revealed that Google Cloud's IaaS performance was 10% higher than AWS or Azure, thanks to the optimized architectures of Vertex AI and BigQuery.
AWS takes a different approach, leveraging its custom silicon - Graviton, Trainium, and Inferentia - to maximize performance-per-dollar for compute-heavy tasks. On the container orchestration front, Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) continues to lead as the most advanced and high-performing managed Kubernetes platform in 2025.
When it comes to network architecture, Google Cloud and Azure prioritize backbone-centric routing. This design reduces latency by routing user traffic into their private networks as close to the user as possible. Meanwhile, AWS has been shifting away from its traditional Internet-centric model, enhancing backbone performance in selected regions.
"Cloud networks are networks just like any other... they're subject to the laws of physics, and they are run by people just like enterprise networks."
- Angelique Medina, Head of Internet Intelligence, ThousandEyes
Before committing to a provider, engineering teams should conduct proof-of-concept tests. Vendors' marketing claims often differ from real-world performance, especially in areas like network egress and latency. These metrics are crucial because they directly impact service level agreements and operational reliability.
Performance is only as good as the reliability backing it. All three providers deliver high reliability for enterprise operations in 2025, but their methods vary. AWS focuses on designing systems that can handle failure, employing chaos engineering and strict change management to minimize disruptions. Azure prioritizes business continuity with a high-availability mindset tailored to specific needs. Google Cloud uses SRE principles, including service level objectives (SLOs) and error budgets, to maintain consistent performance.
For compute services, AWS guarantees 99.99% uptime for multi-AZ deployments, while single-instance deployments come with a 99.5% SLA. Azure and Google Cloud offer SLAs of up to 99.9% for their compute instances. AWS also provides a unique customer assurance: if uptime drops below 95% in a month, customers are eligible for a 100% service credit.
Beyond performance and uptime, security and identity management are essential for dependable cloud platforms. In today’s cloud environments, securing operations is as critical as managing costs and compliance.
Each provider has its own approach to security. AWS offers a mature, granular identity system through IAM, which supports complex hierarchical structures via AWS Organizations. Its Nitro System enhances security by isolating virtualization functions at the hardware level, while GuardDuty uses machine learning to detect malicious activity.
Azure integrates deeply with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), making it a strong choice for enterprise environments. It supports adaptive multi-factor authentication with conditional access policies based on risk. Azure also excels in compliance-heavy industries, offering over 100 certifications, including HIPAA, GDPR, and FedRAMP. Microsoft Defender for Cloud ensures robust security monitoring across multi-cloud and hybrid setups.
Google Cloud adopts a secure-by-default philosophy, providing encryption at rest and in transit automatically. It has been a leader in implementing the BeyondCorp Zero Trust model, which eliminates the need for traditional VPNs - a great fit for distributed teams. Tools like Security Command Center and the AI-powered Chronicle further enhance Google Cloud’s proactive threat detection capabilities.
"Google offers encryption at rest and in transit by default. With AWS and Azure, you've got to enable that feature."
- Adam Zeineddine, Host of HIPAA Insider Show
All three providers operate under a shared responsibility model: they secure the infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their data and configurations. For U.S. businesses, the choice often depends on existing ecosystems. Organizations heavily invested in Office 365 or Windows Server may prefer Azure for its seamless identity solutions. On the other hand, AWS may be better suited for companies needing granular API-level control across vast resources.
AWS is a go-to choice for startups and prototyping, thanks to its wide range of services and extensive ecosystem. With over 200 services and the largest third-party support network, AWS allows US companies to quickly launch and test new ideas. Plus, its vast community of certified professionals - outnumbering Azure and Google Cloud certifications by 3:1 - ensures accessible expertise.
Azure stands out for businesses heavily invested in Microsoft tools and those in regulated industries. If your company depends on Office 365, Windows Server, or Active Directory, Azure’s seamless integration offers unified identity management. It’s also a solid choice for healthcare and financial services, with over 100 compliance certifications, including HIPAA, FedRAMP, and GDPR. Additionally, the Azure Hybrid Benefit can cut Windows workload costs by as much as 40%.
Google Cloud shines for data-driven companies focusing on AI and analytics. If your business thrives on machine learning, real-time customer personalization, or big data analytics, GCP’s tools like BigQuery and Vertex AI deliver strong performance and value. These features are particularly appealing to retail and media industries.
Matching your use case with the right platform ensures alignment with your tech stack, budget, and compliance requirements.
When choosing a platform, consider your existing software ecosystem and financial constraints. For companies using Microsoft 365, Azure offers seamless identity management. On the other hand, businesses that rely on open-source tools or Kubernetes-based applications might prefer Google Cloud, which pioneered Kubernetes and offers the industry-leading GKE platform.
Pay attention to hidden costs. Google Cloud’s transparent pricing includes automatic sustained-use discounts of up to 30%, while AWS provides steep savings - up to 90% - via Spot Instances for flexible workloads.
Compliance needs can also guide your decision. For government-related projects requiring FedRAMP certification, AWS GovCloud or Azure Government regions are excellent options. Additionally, consider your team’s familiarity with each platform. AWS’s learning curve might require more training, while Azure’s interface is intuitive for Microsoft users, and Google Cloud’s developer-friendly design caters to tech-savvy teams.
"The right choice comes down to your organization's specific requirements, existing tech stack, and long-term goals."
- Benito Martin, Founder of Martin Data Solutions
As multi-cloud strategies become the norm, about 89% of US businesses now use multiple cloud providers to reduce vendor lock-in and manage costs effectively. Instead of relying solely on one hyperscaler, companies often mix and match: running compute workloads on AWS, analytics on Google Cloud, or enterprise applications on Azure, while turning to specialized providers for unique needs.
For example, SurferCloud can enhance hyperscale platforms by handling workloads that demand high privacy or low-latency edge computing. This hybrid model allows businesses to keep core infrastructure on major platforms while routing sensitive or latency-critical tasks through specialized providers. Automation tools can further streamline multi-cloud cost management without interrupting operations.
Deciding between AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud in 2025 comes down to your specific business needs - not just platform rankings. Each provider has its strengths: AWS offers an extensive range of services, Azure integrates seamlessly with Microsoft products, and Google Cloud shines in data analytics and AI/ML. The key is to assess how these strengths align with your unique operational requirements.
Test each platform with real-world workloads to identify hidden costs and performance differences. Switching cloud providers later can be both expensive and time-intensive, often costing between $100,000 and $1 million and taking 6–18 months to complete.
Look beyond technical specs and consider how the platform fits your team's expertise and existing tech stack. AWS certifications are widely recognized, but retraining a team can take 3–6 months. If you're running a Microsoft-heavy environment, Azure's Hybrid Benefit could cut Windows workload costs by up to 40%. For businesses prioritizing AI, Google Cloud's pricing model - offering automatic sustained-use discounts of up to 30% - delivers notable savings.
Multi-cloud strategies are becoming the norm, with 89% of US businesses now adopting this approach to reduce vendor lock-in and manage costs effectively. Instead of relying solely on one provider, consider combining services to leverage each platform's strengths. You might also explore specialized providers for specific needs like edge computing or high-privacy workloads.
When selecting a cloud platform, it’s crucial to match the provider’s strengths with your business needs. AWS is known for its extensive range of services and a strong third-party ecosystem, making it a solid choice for businesses handling diverse workloads or those looking for early access to cutting-edge features. If your company relies heavily on Microsoft tools like Windows Server, Office 365, or Active Directory, Azure offers seamless integration and excels in hybrid-cloud setups. Meanwhile, Google Cloud is a standout option for data-heavy projects, AI/ML applications, and its intuitive Kubernetes platform.
Beyond these core strengths, take a closer look at factors like pricing structures, global reach, and usability. All three providers offer flexible billing options, but their cost-saving mechanisms vary, so estimating your usage is key to understanding the overall expense. Also, consider the number of regions and availability zones available, which can impact latency and compliance. Finally, evaluate the learning curve and support services each platform provides. Weighing these elements carefully will help you identify the platform that best meets your business objectives.
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud all operate on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, but they differ in how they handle discounts and free-tier benefits.
Each platform has its strengths: AWS stands out with its variety of discount options, Azure combines flexible pricing with credits and reservations, and Google Cloud emphasizes upfront credits and simplicity to make it easier for new users to get started.
Businesses are increasingly adopting multi-cloud strategies because they provide more flexibility and resilience. By working with multiple cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, companies can sidestep vendor lock-in, manage costs more effectively, and tap into the unique strengths each platform offers. For instance, Azure’s hybrid tools can be ideal for certain setups, AWS delivers a wide range of services, and Google Cloud excels in AI and machine learning capabilities.
This strategy also boosts operational efficiency. It lowers infrastructure maintenance expenses, enhances reliability with better availability, and ensures scalability to meet spikes in demand. On top of that, multi-cloud setups improve security by spreading out risk and give businesses access to the latest technologies from various providers, helping them stay innovative and agile as they navigate 2025.
December is always a busy month for developers, online ...
With Southeast Asia’s growing demand for online servi...
Black Friday is the best time to migrate your cloud inf...