SurferCloud GPU UHost: Deploy Your DeepSeek R
DeepSeek-R1 is an open-source reasoning model designed ...







Cloud costs can spiral out of control if not managed effectively. On average, 32% of cloud budgets are wasted, often due to idle resources, over-provisioning, and inefficient usage. However, you can significantly reduce your cloud expenses with the right strategies. Here’s what you need to know:
These strategies, when applied together, can cut cloud costs without sacrificing performance. Start by auditing your current usage, eliminate waste, and implement solutions like auto-scaling and resource tagging for better cost control.
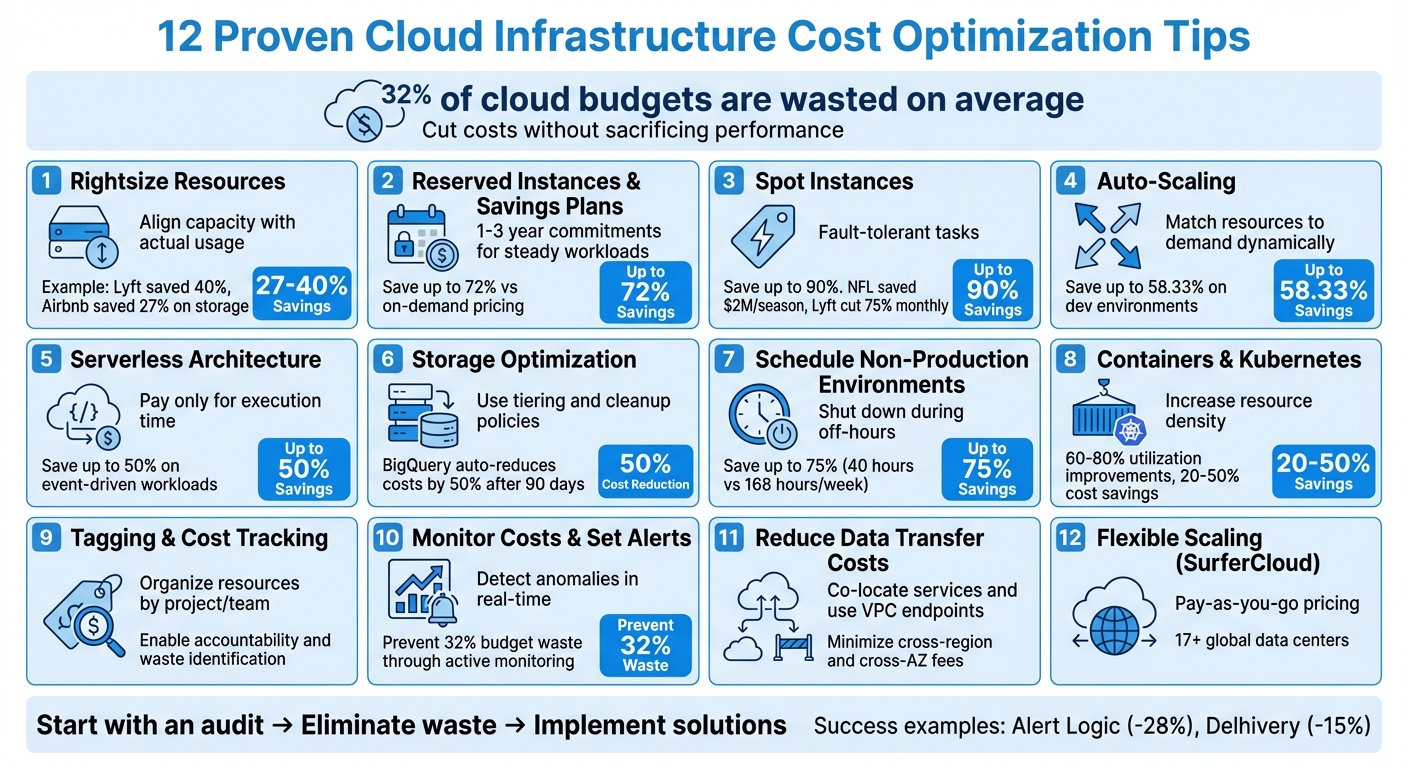
12 Cloud Cost Optimization Strategies with Potential Savings
Rightsizing is all about aligning your server instances and storage capacities with the actual demands of your workloads. It’s a straightforward way to avoid paying for resources you don’t use. Overprovisioning - like choosing larger servers "just in case" - often results in idle vCPUs and memory, leading to unnecessary costs.
"Right-sizing enables you to analyze computing services and modify them to the most efficient size." – Spot.io
To start, implement a structured monitoring process. Track resource usage - like vCPU, memory, network throughput, and disk I/O - for at least two weeks. This helps you capture peak traffic periods. If your highest usage is consistently below 80% of a smaller instance’s capacity, consider scaling down. Development and testing environments are often the biggest culprits here. They typically run 24/7 but are actively used only during work hours, wasting 60–66% of their costs.
The results of rightsizing can be dramatic. In 2021, Lyft slashed cloud costs by 40% by fine-tuning their resource allocation. Similarly, Airbnb saved 27% on storage and 60% on Amazon OpenSearch by analyzing usage patterns and optimizing accordingly.
Another key step is eliminating "zombie" resources - things like unattached storage volumes, stale snapshots, idle load balancers, and unassociated Elastic IP addresses. These can quietly rack up charges. For storage, switching from GP2 to GP3 volumes can cut costs by up to 20% without reducing capacity. You can also save more by setting up lifecycle policies to move rarely accessed data to cheaper options like S3 Glacier.
Keep in mind that rightsizing isn’t a one-and-done effort. Workloads evolve, new instance types become available, and business needs shift. Make it a habit to review your resources monthly. Tools like AWS Compute Optimizer, AWS Trusted Advisor, and Amazon CloudWatch can help you monitor usage trends and adjust accordingly.
If you're running consistent workloads like production databases, web servers, or backend APIs, relying on on-demand pricing can drain your budget. This is where Reserved Instances (RIs) and Savings Plans (SPs) come in. By committing to use a certain amount of resources for one or three years, you can significantly reduce costs - up to 72% savings compared to on-demand pricing. Of course, this means trading some flexibility for those cost reductions.
Here's how they differ: Reserved Instances lock you into specific configurations - such as instance type, region, and tenancy - for the duration of your contract. Savings Plans, on the other hand, are more flexible. You commit to spending a fixed hourly amount (e.g., $10), and that commitment automatically adjusts across various instance types, regions, and even services like Fargate and Lambda.
"Reserved Instances are based on the commitment to use an instance at a particular price over a specific period, while Savings Plans are based on the commitment to spend a particular dollar amount per hour over a specific period" – Didier Durand
For compute workloads, Savings Plans are often the better choice since they offer similar discounts with less administrative hassle. However, for database services like RDS, Redshift, or ElastiCache, Reserved Instances remain the go-to option because Savings Plans currently don't cover those services.
When purchasing, you have three payment options:
These payment structures let you align costs with your predictable resource needs.
Examples from real-world use cases highlight the benefits. Alert Logic reduced costs by 28%, while Delhivery cut infrastructure expenses by 15% by gradually increasing commitments and centralizing discount management. Instead of making one large upfront commitment, consider purchasing incrementally. This ensures your coverage adapts as your workloads evolve. Also, use a management account without resources of its own to centralize discounts, automatically applying them to the highest-cost usage across linked accounts.
Reserved Instances and Savings Plans are ideal for steady-state workloads - applications running 24/7 with stable resource demands. For short-term projects (less than a year) or workloads with unpredictable spikes, sticking with on-demand pricing is the safer bet. To make informed decisions, use tools like AWS Cost Explorer to analyze past usage and get automated recommendations on how much to commit. Just make sure to rightsize your instances beforehand - there’s no benefit in locking in discounts for oversized resources.
Spot instances can save you up to 90% compared to on-demand rates. However, they come with a catch - providers can reclaim them with just a two-minute warning. The good news? Spot instances are interrupted less than 5% of the time on average, and while they’re active, they perform just as well and are just as secure as on-demand instances.
These instances are perfect for stateless, fault-tolerant workloads. Think batch jobs, big data analytics, containerized applications, CI/CD pipelines, high-performance computing (HPC), and test environments.
The savings can be staggering. For example, the National Football League (NFL) has been using 4,000 spot instances across more than 20 instance types since 2014 to build its intricate season schedule. This approach has saved the NFL $2 million every season and more than $20 million in total [25, 27]. Similarly, Lyft slashed its monthly compute costs by 75% by tweaking just a few lines of code to support spot instances [25, 28]. Delivery Hero, another success story, reduced costs by 70% by running Kubernetes clusters on spot instances [25, 28]. These examples highlight how businesses can dramatically cut expenses while maintaining efficient operations.
To reduce the risk of interruptions, follow a few best practices:
For added security, consider checkpointing to save progress to persistent storage. If your workload is time-flexible, configure your instances to stop or hibernate instead of terminate. This way, they can resume automatically when capacity becomes available.
Keep in mind, spot instances are not included in Savings Plans. For steady workloads, rely on Reserved Instances or Savings Plans, and use spot instances to handle flexible, burst capacity needs.
Auto-scaling is a smart way to manage resources, automatically adjusting capacity based on traffic. It adds resources during high-traffic periods and scales them down during quieter times, helping you avoid unnecessary costs.
For instance, shutting down development environments outside of business hours (8 AM–6 PM) can save up to 58.33% of weekly costs. For production workloads with fluctuating traffic, combining auto-scaling with Spot Instances can slash costs by as much as 90% compared to On-Demand pricing. Adding Savings Plans into the mix can further reduce expenses by up to 72%.
This approach has shown success across many types of workloads.
"The goal of cost optimizing scaling is to scale up and out at the last responsible moment and to scale down and in as soon as it's practical." - Microsoft Azure
To configure auto-scaling, you’ll need to define minimum, maximum, and target capacities. Base your scaling metrics on factors like CPU, memory, or network usage. For predictable traffic patterns, scheduled scaling works well, while dynamic scaling with target tracking is ideal for variable traffic. Be sure to set cooldown periods to avoid frequent, unnecessary scaling adjustments.
Auto-scaling is especially effective for stateless web servers, batch processing, periodic applications, and development environments. The service itself typically doesn’t come with additional charges - you only pay for the compute resources you use.
Serverless computing changes the game when it comes to cost efficiency. Instead of paying for idle time, you’re only charged for actual execution time - down to the millisecond. This means you’re only paying for what you use, which can significantly cut costs.
This model works especially well for unpredictable, event-driven workloads like API calls, image processing, or generating automated reports. Serverless platforms automatically scale resources to meet demand, going from zero to full capacity and back down again once the workload is done. For tasks that happen in short bursts, this approach can save more money compared to running virtual machines around the clock.
"Cloud cost management increasingly focuses on architectural optimization. Through this lens, applications can be built with highly elastic infrastructure, so your company only pays for what you and your customers use." – CloudZero
To get the most out of serverless, fine-tune your function settings. Tools like AWS Lambda Power Tuning let you test different memory and CPU configurations to find the sweet spot between performance and cost. Shorter execution times mean lower bills. Also, aim to keep your deployment packages under 10 MB to reduce cold start delays.
That said, serverless isn’t the best option for everything. For steady-state workloads that run continuously, traditional compute options like Savings Plans or Reserved Instances often offer better value. But for intermittent tasks, serverless can slash operational costs by up to 50% while removing the hassle of managing servers. It’s a great way to complement other cost-saving strategies, especially when dealing with unpredictable workloads.
Storage can quietly become a major contributor to your cloud expenses if not managed carefully. The solution? Organize your data into the right storage tiers and eliminate unused files. By aligning your data with specific tiers - like Standard for frequently accessed data and Archive for long-term storage - you can cut costs significantly. Each tier has its own pricing: hot storage is the most expensive but provides instant access, while archive storage is the most budget-friendly option for rarely accessed data.
The trick lies in matching your data to the correct tier based on its usage. For instance, BigQuery automatically slashes storage costs by 50% for tables that haven’t been modified in 90 days. Tools like AWS S3 Lifecycle and Google Cloud Object Lifecycle Management can automate the process, moving data between tiers based on its age or how often it’s accessed. Once your data is tiered efficiently, take the time to audit and clean up unused storage to avoid unnecessary charges.
Look for storage "zombies" - unattached persistent disks, orphaned snapshots, outdated backups - and set up automated lifecycle rules. For example, you can configure rules to delete log files after 31 days. In data warehouses, using partitioning can also help reduce costs by limiting the amount of data scanned during queries.
"The first step is creating a practice around how to identify the usefulness of an object/bucket to your business." – Justin Lerma, Technical Account Manager, Google Cloud
Start by auditing your storage assets. Keep in mind that while cold and archive tiers offer lower storage costs, they often come with high retrieval fees and minimum retention periods (e.g., 30 days for Nearline). The ideal approach is to tier data that must be retained for compliance or backup purposes but is rarely accessed. This strategy allows you to meet retention requirements without inflating your storage budget.
Once you've adjusted resource sizes and implemented scheduling, the next step to cutting costs is optimizing the runtime of non-production environments. These environments, like development or testing setups, typically run only 40–50 hours a week. Keeping them running 24/7 wastes nearly 70% of their resources and unnecessarily drives up expenses.
A simple solution? Schedule non-production instances to shut down at 5:00 PM and restart at 8:00 AM. This change can reduce weekly runtime from 168 hours to just 40 hours, potentially cutting costs by up to 75%. For example, a higher education institution saw a 30% drop in overall EC2 costs within a month of setting up automatic shutdowns. This scheduled downtime aligns perfectly with other cost-saving strategies, ensuring resources are active only when needed.
There are two main approaches to automation:
Another handy tool is the Instance Scheduler on AWS, which can manage EC2 and RDS instances across multiple regions for around $13.15 per month.
"Development and test environments are typically only used for eight hours a day during the work week. You can stop these resources when they are not in use for a potential cost savings of 75% (40 hours versus 168 hours)." – AWS Well-Architected Framework
To get started, tag your non-production resources with identifiers like AutoStop: True. This helps automation scripts recognize which resources to manage. Focus on development servers, QA setups, training labs, and demo environments - these are prime candidates for scheduling. Be sure to communicate the schedule to your teams and set up a process for exempting instances during critical testing phases.
Boost server efficiency by consolidating workloads with containers and Kubernetes. These tools shine at optimizing resource use through a method called bin-packing - essentially the art of fitting multiple isolated applications onto the same hardware, much like arranging boxes perfectly within a shipping container. This approach enables you to run more workloads on fewer servers compared to traditional virtual machines, setting the stage for dynamic scaling and cost savings.
The potential for cost reduction is impressive. By leveraging Kubernetes’ bin-packing and autoscaling capabilities, organizations can see 60–80% utilization improvements. Grouping workloads into larger clusters and fine-tuning pod allocation minimizes fragmentation and management overhead, which can lead to savings of 20–50%.
Kubernetes supports three key autoscaling methods to optimize resource use:
These autoscaling tools ensure you’re only paying for resources when they’re needed. Pairing autoscaling with Spot instances for fault-tolerant workloads (like batch jobs or CI/CD pipelines) can slash costs by up to 90%.
However, Kubernetes management isn’t without its challenges. A study found that 68% of businesses face difficulties in managing Kubernetes, and only 12% successfully cut costs. The complexity often arises from issues like multi-tenancy, uncontrolled dynamic scaling, and limited visibility into pod-level expenses. To tackle these challenges, it’s crucial to set CPU and memory limits for each container to prevent resource overuse and inefficiencies.
Containerization also plays a key role in reducing waste by allocating resources with precision. Workloads best suited for this approach include stateless microservices that handle fluctuating traffic, batch processing jobs (like big data tasks or media transcoding), and development environments that can be scaled back during off-hours. To get started, set resource limits, use the VPA in recommendation mode for at least 24 hours to identify optimal sizing, and deploy fault-tolerant workloads on Spot instances.
Using tags to organize cloud resources is a smart way to keep track of spending and ensure accountability. Tags allow you to sort costs by project, team, environment, cost center, or application, providing detailed visibility into where your money is going. This level of clarity can lead to better financial decisions, like allocating more funds to high-performing, revenue-generating applications while cutting back on underperforming projects.
Once you’ve nailed down accurate cost tracking, consider implementing showback and chargeback models. These methods report costs by team or project, encouraging more efficient use of resources and cutting down on unnecessary expenses. The AWS Well-Architected Framework highlights the importance of this approach: "The capability to attribute resource costs to the individual organization or product owners drives efficient usage behavior and helps reduce waste". Tags, when paired with lifecycle tracking, can also help pinpoint orphaned resources - those forgotten instances still running long after their intended use.
Focus first on tagging your highest-cost resources, such as compute instances, networking components, and storage buckets. It’s also a good idea to tag development and testing environments separately. This makes it easier to identify and manage non-critical workloads.
To make tagging effective, establish a consistent set of tag keys and values. Examples might include Environment: Production, Team: Marketing, or CostCenter: ENG-001. Use tools like Infrastructure as Code to automate tag application during resource provisioning, and enforce policies that block the creation of resources without the necessary tags. Keep in mind that tags aren’t retroactive - you’ll need to activate them in your billing console for them to show up in future cost reports.
Finally, monitor tagged resources in real time. Keep an eye on metrics like CPU, memory, and network usage to quickly identify and scale down underutilized instances. For more complex account setups, you can use cost categories to group multiple tags into broader business dimensions, making your reporting cleaner and more organized.
Keeping an eye on your cloud costs in real time is essential if you want to avoid unnecessary spending. In fact, without real-time monitoring, you could be wasting as much as 32% of your cloud budget. By actively tracking expenses, you can set up automated alerts that help you stay within budget.
Set spending alerts at different levels - whether it's for an account, a specific service, or a project - based on both current and projected costs. Notifications can be sent through email, SMS, or tools like Slack, ensuring the right team members are informed immediately.
Leverage machine learning to identify unusual spending patterns by analyzing historical usage. Keep an eye on technical metrics like CPU usage, memory, network activity, and idle resources. This allows you to spot inefficiencies and figure out whether cost increases are due to genuine growth or misconfigured resources.
To make these alerts even more effective, monitor costs daily instead of relying on monthly summaries. This way, you can take action within hours rather than waiting weeks. For critical workloads, consider automating responses to shut down or resize idle resources based on real-time data. This proactive approach can save both time and money.
Data transfer fees can add up quickly when services operate across different regions or availability zones. Transfers between regions come with the highest per-gigabyte charges, while cross-availability zone (AZ) transfers incur moderate fees. However, transfers within the same AZ are often free.
To minimize these costs, consider co-locating services that frequently communicate. For instance, placing your database read replicas in the same AZ as your application instances can help avoid cross-AZ transfer fees. Similarly, if you're dealing with services that exchange significant amounts of data - like compute instances accessing object storage or container registries - using VPC endpoints ensures that traffic stays within the provider's private network, avoiding expensive egress charges.
Take this a step further by analyzing your data flows to identify where transfer costs are highest. Before moving any services, map out your data transfer patterns to pinpoint the most expensive routes. Use cost management tools to break down spending by region and usage type, and focus on consolidating high-traffic services into the same AZ. Regularly monitor network metrics to uncover costly transfer routes.
"Efficient use of networking resources is required for cost optimization in the cloud." – AWS
It’s important to note that co-location comes with a trade-off: reduced resiliency. While it cuts costs, it also increases vulnerability to zone-level outages. For production workloads that demand high availability, you'll need to weigh these savings against your recovery time objectives. Co-location works best as part of a broader cost-reduction strategy, targeting hidden data transfer expenses without compromising critical operations.
SurferCloud's Elastic Compute Servers bring together smart cost-saving strategies in a flexible, scalable platform. With a pay-as-you-go pricing model, you’re only charged for the compute resources you actually use. This transforms infrastructure spending into an operational expense that grows or shrinks with your business needs, avoiding the trap of overprovisioning for peak times and wasting money during slower periods.
The platform supports both vertical scaling (adjusting the size of instances) and horizontal scaling (adding or removing instances), making it easy to match your resources to your workload demands. Plus, with deployment options across 17+ global data centers, you can reduce latency and cut down on data egress fees. These features work hand-in-hand with earlier strategies, offering seamless cost control.
By combining features like reserved instances and auto-scaling, SurferCloud ensures your costs align perfectly with demand. Real-time rightsizing further optimizes spending by eliminating idle capacity - you only pay for what you use.
Take e-commerce businesses, for example. During seasonal surges like Black Friday, they can scale up compute capacity to handle the load and then automatically scale back afterward, avoiding unnecessary costs. Startups and small businesses love this model because it eliminates the need for hefty upfront investments. For SaaS providers, it’s a game-changer, allowing cloud expenses to grow alongside customer demand.
When paired with the earlier 11 strategies - from reserved instances to storage tiering - SurferCloud's elastic servers become a cornerstone of a well-rounded cost optimization plan.
Managing cloud costs isn’t a one-and-done task - it’s an ongoing effort to cut waste and make the most of every dollar spent. The strategies outlined - like rightsizing, reserved instances, auto-scaling, and leveraging SurferCloud's elastic compute servers - work together as a solid plan for keeping cloud expenses under control.
The benefits of regular cost monitoring are clear. For instance, Alert Logic slashed costs by 28%, while Delhivery managed to save 15% in just 50 days. These examples highlight that a continuous approach to optimization delivers far better results than quick, one-time fixes.
"Cloud cost optimization is not a one-time event, but rather an ongoing strategy with a myriad of benefits - from a more cost-effective cloud environment to a more competitive business." - Fadeke Adegbuyi, Manager, Content Marketing, DigitalOcean
Start by auditing your cloud spending. Identify idle resources, set up threshold alerts, and tag resources by department or project. Then, implement technical strategies like rightsizing, scheduling shutdowns for non-production environments, and using reserved instances for predictable workloads. These steps encourage a proactive mindset toward managing costs.
To sustain results, make cost optimization part of your routine. Review usage every month and adjust strategies to align with your business’s changing needs. Quick wins - like eliminating unused resources - paired with longer-term solutions such as Savings Plans (which can save up to 72%) create a strong foundation for lasting efficiency. By staying proactive, you’ll keep cloud spending in check as your business grows and evolves.
To manage cloud costs effectively through rightsizing, start by keeping a close eye on your resources for 14 to 30 days. This will help you uncover their typical and peak usage patterns. Focus on key metrics like CPU, memory, network, and disk usage. Look for resources that are consistently underused - such as instances operating below 50–70% of their capacity.
Once you've pinpointed these underutilized resources, switch to a smaller instance type that better fits your workload needs without compromising performance. Before committing, test the new instance in a staging environment to confirm it meets your expectations. Simplify the process by automating regular reviews, leveraging tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Budgets, and tagging resources to improve tracking. By staying proactive with monitoring and adjustments, you can keep your cloud expenses in check while ensuring optimal performance.
Reserved Instances (RIs) are tailored for workloads that are steady and predictable. With RIs, you commit to a specific instance type, size, operating system, tenancy, and AWS region for a duration of one or three years. In return, you can enjoy discounts of up to 72% compared to On-Demand pricing. However, this level of commitment comes with less flexibility - if your requirements shift, you'll need to either exchange or modify your reservation.
Savings Plans take a different approach by offering more flexibility. Instead of committing to specific resources, you agree to a consistent dollar-per-hour spend on eligible compute services. This agreement automatically adjusts to match your usage across various instance families, sizes, operating systems, tenancy, and even regions, delivering discounts of up to 66-72%. While the savings might not always match those of RIs, Savings Plans are a great fit for workloads that fluctuate over time or span multiple resources.
RIs are best for maximizing savings on fixed, predictable workloads, whereas Savings Plans shine when flexibility and adaptability are key.
Auto-scaling is a smart way to manage cloud costs by automatically adjusting your resources to match demand. This means you only pay for what you actually use. To make the most of it, here's how you can set it up:
Keep an eye on your system's performance and expenses regularly. Fine-tuning your auto-scaling setup helps you adapt to changing workloads, avoid resource waste, and keep your cloud spending under control - all while maintaining solid performance.
DeepSeek-R1 is an open-source reasoning model designed ...
? Pain Point Most developers using WebRTC depend on ...
When it comes to Forex trading, the location of your se...