HTTP vs HTTPS: Why SSL Certificates Matter fo
In today’s digital world, ensuring the security of on...






AI-driven maintenance outperforms older methods by focusing on equipment condition rather than fixed schedules, delivering fewer disruptions and higher accuracy.
Key takeaway: Start small - pilot AI tools on critical assets to reduce costs and boost reliability.
AI-driven predictive maintenance is reshaping how factories operate by focusing on the actual condition of equipment rather than sticking to fixed schedules or waiting for breakdowns. Using sensor data - like vibration, temperature, and pressure - this approach ensures maintenance happens only when necessary. It cuts down on wasted resources from replacing perfectly functional parts and minimizes the risk of unexpected failures. The result? A significant reduction in downtime and smoother operations.
One of the standout benefits of predictive maintenance is its ability to slash unplanned downtime by 30% to 50% through early problem detection - weeks before issues arise [7]. This foresight allows factories to handle repairs during scheduled breaks, steering clear of disruptive emergency shutdowns. For example, in 2022, Deloitte partnered with a major logistics provider to tackle equipment failures in distribution centers. By installing sensors and analyzing data in the cloud, they could predict equipment lifespans across the network. This enabled targeted maintenance, leading to quicker operations and a competitive edge in the market [9].
Edge computing takes this efficiency even further by processing data right on the factory floor. This cuts response times from hours to just milliseconds [7]. For high-speed machinery, such instant analysis is critical - it can detect and address anomalies before they escalate into major production issues.
Predictive maintenance doesn't just save time - it saves money too. By optimizing resource use, it reduces costs by 15% to 25% [10][7]. Instead of replacing parts based on a schedule, components are replaced only when needed, avoiding unnecessary expenses. Plus, it prevents the domino effect where one failing part damages nearby machinery, which can lead to costly emergency repairs.
"Predictive maintenance promises to provide the best of both worlds by aiming to reduce unnecessary preventive maintenance while ensuring that assets don't face catastrophic failure." - Deloitte [4]
This approach also streamlines spare parts management. With "just-in-time" procurement, companies can avoid tying up capital in large on-site inventories [7][9]. Additionally, by keeping machines in optimal condition, their lifespan increases by 20% to 25%, further lowering the overall cost of ownership [7].
AI models bring a 35% boost in predictive accuracy over traditional methods by combining data from multiple sources with advanced analytics [10]. Tools like physics-informed AI and Digital Twin technology can spot anomalies that simpler systems or human operators might miss. This level of precision ensures that even subtle issues are caught early.
The benefits don’t stop there. Predictive accuracy feeds directly into automation. For instance, when AI identifies a potential failure, it can automatically initiate actions - like generating purchase orders for spare parts in ERP systems or scheduling technicians through Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) [4]. This closed-loop process ensures that predictions lead to immediate, effective responses, improving overall efficiency and agility.
For large-scale manufacturing, AI-driven maintenance can be scaled effectively. Edge computing nodes process data locally, reducing the strain on central servers [7][11]. In cases where failure data is scarce, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can create synthetic data to train models on rare defects [3].
Digital Twin technology plays a key role in scaling operations by monitoring interconnected assets across multiple facilities simultaneously, rather than treating machines as isolated units [10][9]. Cloud-based platforms like SurferCloud (https://surfercloud.com) provide the infrastructure to handle these complex systems, ensuring reliability and consistent performance across vast networks. This scalability is a cornerstone of the smart factory revolution, enabling manufacturers to harness AI-driven maintenance on a broader scale.
Traditional maintenance methods, while once the backbone of industrial operations, now highlight their limitations when compared to AI-powered alternatives. These methods, though still widely used, often struggle with inefficiencies and high costs. They generally fall into two main categories: reactive maintenance (run-to-failure) and preventive maintenance (time-based servicing). Both approaches force manufacturers into a tough spot - balancing the need to keep equipment running longer with the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
"Traditionally, this dilemma forced most maintenance organizations to choose between two options: Maximizing the run time of an asset at the risk of asset downtime (run-to-failure) or maximize reliability of an asset through early replacement of potentially good components (time-based preventive maintenance)." – Deloitte [4]
Reactive maintenance operates on the principle of waiting until something breaks before fixing it. The downside? It often leads to unplanned downtime, which can be incredibly costly. Industrial manufacturers, for example, lose about $50 billion annually due to unexpected downtime [4].
Preventive maintenance aims to minimize these risks by scheduling regular servicing - say, every 500 hours of operation - regardless of whether the equipment actually needs it [12]. The problem is, these schedules are often based on manufacturer recommendations or informal expertise rather than real-time data. This means maintenance can be performed unnecessarily, wasting both time and resources [4][9].
The financial impact of traditional maintenance approaches is hard to ignore. Reactive maintenance may stretch the life of a part to its limit, but it comes with the risk of catastrophic failures, like overheating or complete breakdowns, which require costly emergency repairs [4][13]. On the other hand, preventive maintenance often replaces parts that are still functional, leading to unnecessary spending on replacements and maintaining a larger inventory of spare parts [4][13].
These inefficiencies can reduce a facility's productive capacity by 5% to 20% [4][5]. Additionally, the reliance on manual data collection and analysis not only drives up labor costs but also slows down decision-making processes [4].
Traditional methods struggle with predicting failures accurately. Time-based maintenance relies on averages and manufacturer guidelines, which fail to account for real-world factors like operating conditions, workload variations, or subtle signs of wear and tear [14][4][5]. Rules-based systems, which use fixed thresholds and ISO standards, often miss the early warning signs of potential issues [5].
Scaling traditional maintenance practices across large operations is a major hurdle. In facilities with thousands of assets, manual inspections and data collection require significant labor [14][4]. Each type of equipment demands specialized knowledge, making organizations heavily reliant on informal expertise that is difficult to share or replicate [4]. Manual record-keeping further complicates matters, often leading to incomplete or inaccurate data that hinders the ability to identify trends or improve processes systematically [3]. As operations grow, the labor-intensive nature of these methods becomes unsustainable, limiting a company's ability to expand while maintaining equipment reliability.
These challenges underscore why many manufacturers are turning to smarter, AI-driven solutions to address the inefficiencies of traditional maintenance methods.
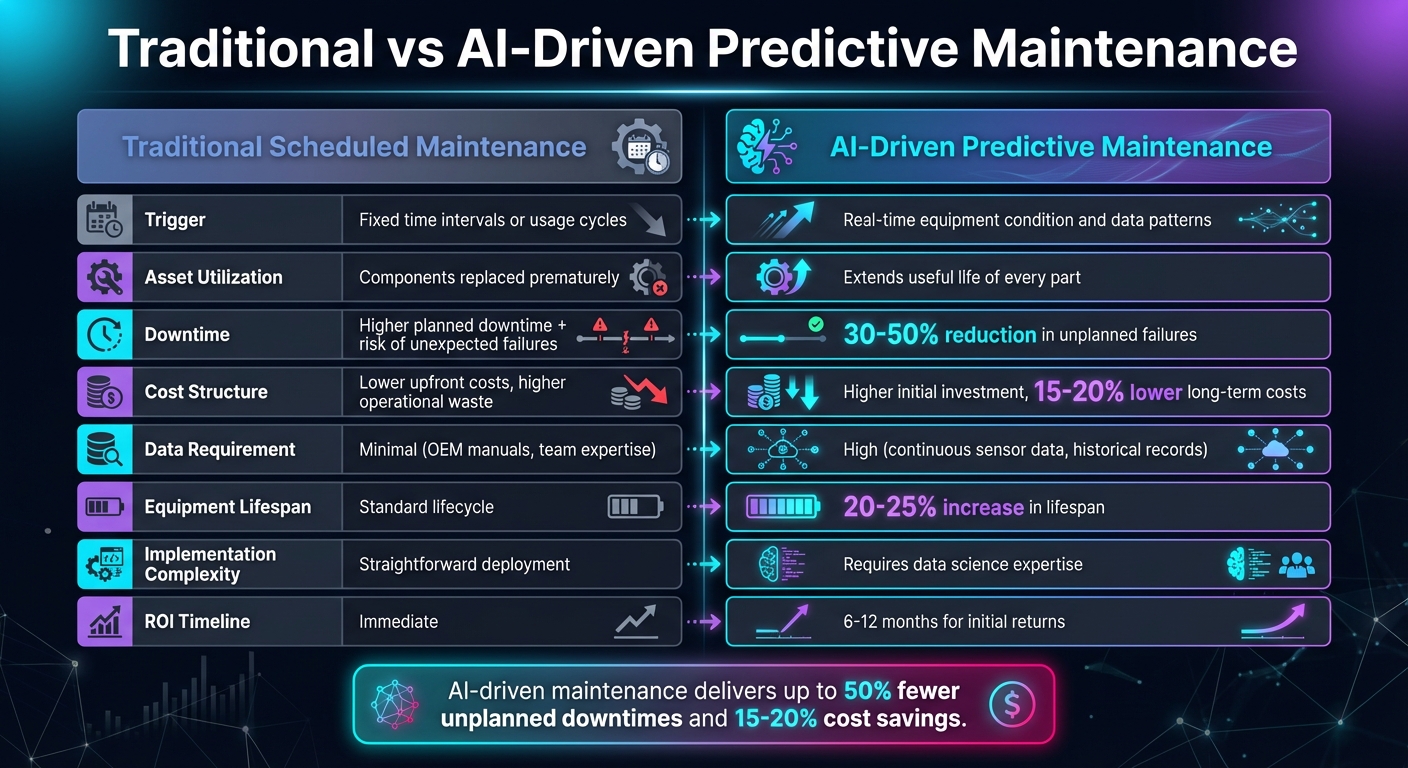
AI-Driven vs Traditional Maintenance: Key Performance Metrics Comparison
When comparing AI-driven predictive maintenance with traditional scheduled maintenance, the differences highlight the evolving needs of modern factories. These two approaches come with distinct trade-offs, which are crucial for shaping maintenance strategies in smart manufacturing environments. The table below outlines how these methods compare across key operational factors.
| Feature | Traditional Scheduled Maintenance | AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Trigger | Based on fixed time intervals or usage cycles | Driven by real-time equipment condition and data patterns |
| Asset Utilization | Components are often replaced prematurely | Extends the useful life of every part |
| Downtime | Higher planned downtime with the risk of unexpected failures between cycles | Reduces planned downtime and cuts unplanned failures by 30%–50% [7] |
| Cost Structure | Lower upfront costs but higher operational waste | Higher initial investment, offset by 15%–20% lower long-term maintenance costs [7] |
| Data Requirement | Minimal, relying on OEM manuals or team expertise | High, requiring continuous sensor data and historical records |
| Equipment Lifespan | Follows a standard lifecycle | Increases lifespan by 20%–25% [7] |
| Implementation Complexity | Straightforward to deploy | Requires advanced data science expertise [8] |
| ROI Timeline | Immediate | Initial returns typically seen within 6 to 12 months [7] |
AI-driven maintenance clearly offers substantial benefits, including up to 50% fewer unplanned downtimes and 15%–20% cost savings [7]. These gains are largely enabled by edge computing, which processes data in real time to deliver actionable insights.
However, achieving these results isn’t without challenges. The biggest obstacle isn’t the technology itself - it’s data quality and change management. Poor historical data can undermine the accuracy of AI models, while insufficient change management can create resistance among maintenance teams [3]. Building trust in AI-generated insights requires targeted workforce training, a step that many companies overlook.
For manufacturers, the key to success lies in assessing whether their infrastructure, data quality, and organizational readiness can support AI adoption. A practical starting point is to run pilot programs on one or two critical assets. These pilots help establish baseline algorithms and demonstrate ROI, making it easier to scale the approach across the entire operation [4].
The evolution from traditional maintenance methods to AI-powered predictive systems is reshaping how smart factories operate. In the past, corrective maintenance meant waiting for equipment to fail, while preventive maintenance often led to prematurely replacing parts that still had useful life - an approach that wasted both time and resources. AI-driven maintenance flips this script, enabling precise, condition-based actions that boost uptime and cut costs.
With edge computing, factories gain the ability to respond almost instantly - essential for high-speed production lines - while keeping sensitive data secure. By processing information locally, edge computing ensures that proprietary operational data stays within the factory, addressing concerns about sending critical information to external servers [2][15].
On top of this real-time precision, cloud platforms like SurferCloud step in to handle tasks that edge devices alone can't manage. With over 17 global data centers and adaptable infrastructure, cloud services analyze massive datasets, uncover long-term performance trends, retrain AI models with updated data, and optimize maintenance strategies across entire operations [1][2]. This hybrid cloud-edge setup creates a powerful partnership: edge devices deliver immediate protection, while the cloud enables advanced analytics and cross-facility coordination [6][2][15]. Together, they ensure both real-time reliability and long-term strategic improvements.
For manufacturers looking to embrace this shift, the path forward is clear: start with critical assets, integrate AI tools with existing CMMS or ERP systems, and focus on maintaining high-quality data [7][4]. The results speak for themselves - companies have reported returns on investment as high as 900% [2]. The real question isn't whether AI will transform factory maintenance, but whether your organization will take the lead or risk being left behind.
AI-powered maintenance takes a forward-thinking approach by leveraging machine learning to analyze real-time sensor data and anticipate equipment issues before they happen. This means factories can plan repairs ahead of time, sidestepping unexpected breakdowns and keeping production on track.
Thanks to edge computing, much of this analysis happens right on-site. This setup speeds up decision-making and minimizes dependence on external networks. By moving from a reactive to a predictive maintenance model, smart factories can run more smoothly, cut expenses, and keep essential machinery running longer.
Edge computing is transforming predictive maintenance by bringing data processing right to the factory floor, near the equipment itself. Sensors gather real-time data and send it to nearby edge devices, where lightweight AI models analyze the information on the spot. These models can quickly identify anomalies, estimate how long equipment will last, and send out alerts - all without depending on distant cloud servers. This approach cuts down on delays caused by network latency and minimizes bandwidth usage.
With real-time analysis happening directly at the source, manufacturers can keep a close eye on equipment health around the clock. They can make immediate adjustments - like tweaking settings or scheduling maintenance - without disrupting operations. At the same time, edge devices share condensed insights with cloud platforms, such as SurferCloud’s scalable infrastructure. This allows manufacturers to store historical trends, conduct long-term analyses, and optimize performance across their entire fleet. By combining fast, localized processing with the cloud’s advanced analytics, this hybrid setup delivers both immediate action and strategic improvements.
To implement AI-driven maintenance effectively, manufacturers should begin by assessing their data readiness. Start with an audit of existing sensors and evaluate the quality of the data they generate. If there are gaps, consider adding affordable IoT sensors and deploying edge-computing nodes. These nodes process data locally, cutting down on latency, saving bandwidth costs, and enabling real-time insights.
The next step is running a small-scale pilot on a critical asset or production line. Use the locally processed data to train predictive models, such as anomaly detection or algorithms for estimating remaining useful life. Compare the model’s predictions with actual maintenance events to validate its accuracy. Bring together cross-functional teams - maintenance engineers, IT experts, and data scientists - to refine the system and ensure smooth integration with existing tools like CMMS or ERP platforms.
Once the pilot delivers measurable results, such as a reduction in unplanned downtime (a problem that costs U.S. manufacturers billions each year), expand the solution across the facility. Use a secure, high-performance cloud platform like SurferCloud to store sensor data, host predictive models, and provide scalable computing resources. Maintain continuous monitoring of model performance, retrain models with updated data when necessary, and enforce strong data security measures. By following this step-by-step approach, manufacturers can unlock significant cost savings and boost operational efficiency.
In today’s digital world, ensuring the security of on...

Data centers must meet strict GDPR rules to protect per...
With an increasing number of browsers to choose from, m...