Top 5 AI Tools for Multi-Cloud Workload Autom
Managing multi-cloud environments is complex. From inco...







Cloud storage costs have been rising due to global supply shortages and increased demand from AI data centers. Many businesses face unexpected fees and inefficiencies, but there are clear strategies to save money without sacrificing performance. Here are five effective ways to reduce your cloud storage expenses:
These methods, when combined, can significantly lower your cloud storage expenses while improving efficiency. Businesses like Zalando and Teespring have already achieved savings of 30-37% using these techniques. For further savings, providers like SurferCloud offer tools to simplify implementation and management.
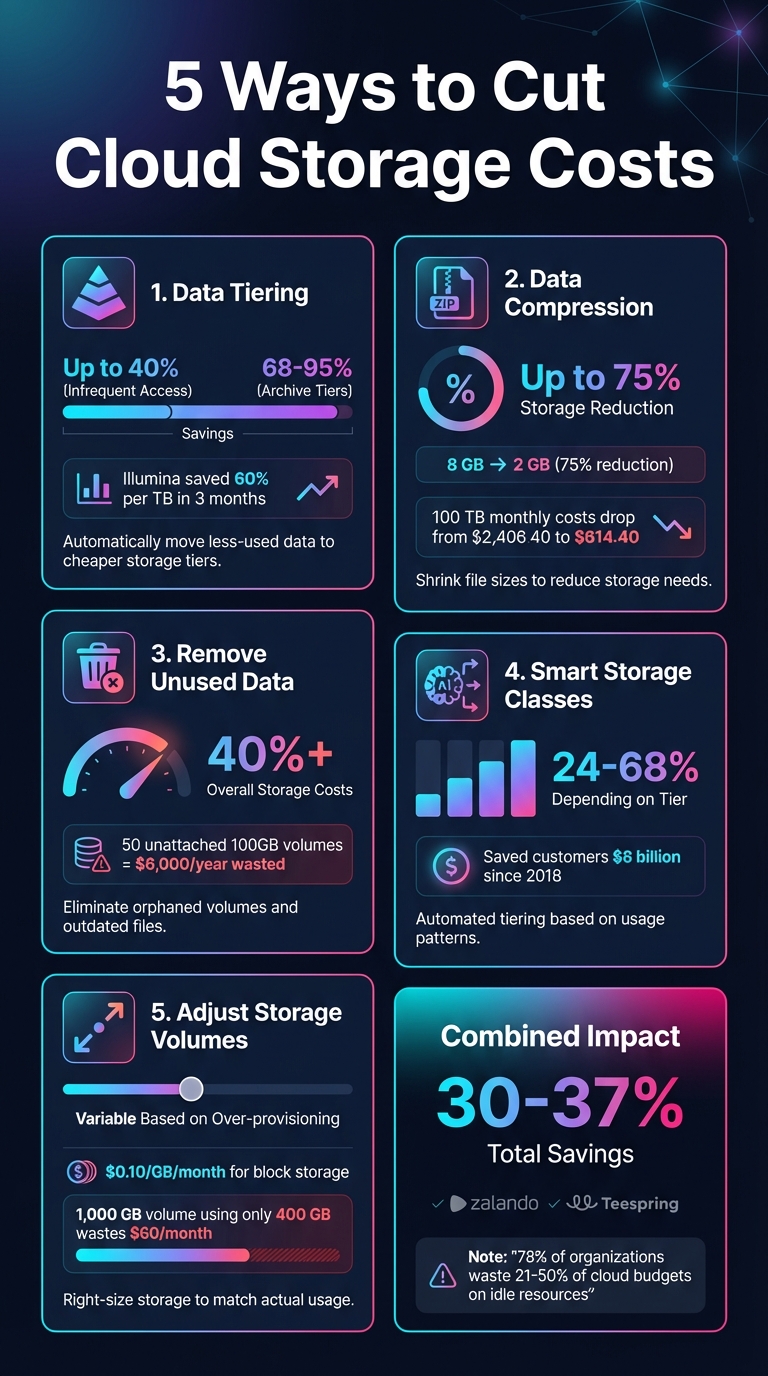
5 Cloud Storage Cost Reduction Strategies with Savings Percentages
Data tiering organizes files based on how often they're accessed, ensuring you're only paying for the level of performance your data actually needs. In cloud storage, intelligent tiering automates this process, making it a go-to strategy for cutting costs.
Switching data from frequent-access tiers to infrequent-access or archive tiers can lead to major savings - up to 40% for infrequent access and 68–95% for archive tiers[4][6]. For example, in 2021, Illumina managed to slash its storage costs by 60% per terabyte within just three months of using intelligent tiering[6].
"We are saving 37% annually in storage costs by using Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering to automatically move objects that have not been touched within 30 days to the infrequent-access tier."
– Max Schultze, Lead Data Engineer, Zalando [4][6]
Modern tiering systems have made the process incredibly straightforward. By setting up lifecycle policies - like automatically moving data after 30 days of inactivity - you can let the platform handle the rest. Torc Robotics, for instance, reduced its monthly storage costs by 24% for its massive petabyte-scale vehicle data using automated tiering. Justin Brown, Head of Vehicle Data Acquisition at Torc Robotics, described it as their "easy button" for achieving rapid results without adding extra development work[6].
Automated tiering continuously tracks how often data is accessed, ensuring you’re not paying for high-performance storage that you don’t need. Electronic Arts utilized this approach to manage tens of petabytes of telemetry data with unpredictable access patterns, cutting storage costs by 30%[6].
Once set up, data tiering scales effortlessly as your storage needs grow. Shutterstock leveraged this to optimize its massive image catalog, saving up to 60% on specific storage buckets. These savings allowed Shutterstock to reinvest in replicating their storage environment in a second region, boosting durability. Chris S. Borys, Team Manager of Cloud Storage Services at Shutterstock, highlighted how this approach made a noticeable difference in their operations[6].
Expanding on tiering strategies, enabling data compression is another effective way to cut storage costs. By shrinking file sizes, compression directly reduces the amount of storage needed, which translates into noticeable cost savings over time.
The financial benefits of compression can be impressive. Take an 8 GB CSV dataset as an example: using a tool like bzip2, you can compress it down to just 2 GB - a 75% reduction in storage size[3]. Now, imagine applying this to a larger dataset, say 100 TB. Monthly storage expenses could drop from $2,406.40 to just $614.40[3]. Beyond storage savings, compression formats like Parquet can slash query costs as well. For instance, a single query that costs $0.10 could be reduced to only $0.001[3].
Most cloud platforms make compression easy with built-in tools and APIs that can handle the process automatically during data ingestion. For high-volume data streams, libraries like the Kinesis Producer Library can aggregate and compress records on the fly, cutting costs by up to 95% for these types of workloads[3]. Serverless services can also convert raw data into compressed formats like Parquet or ORC on a schedule, requiring minimal manual effort[3].
Compression is especially effective for text-heavy files, logs, and columnar data formats. Formats like Parquet and ORC store data column by column, which allows for more efficient encoding and compression[7]. While compression does increase CPU usage, it’s a trade-off that works well for "cold" data that’s rarely accessed[7]. For data that’s queried more often, the savings in scanning costs often outweigh the additional CPU load.
Just like tiered storage, automated compression grows effortlessly with your data. Once set up, it adjusts to larger volumes without extra effort. Choosing compression formats that support parallel processing ensures performance remains strong as data scales[3]. Pairing compression with lifecycle policies can automate the movement of older data into colder, compressed storage[7]. This also reduces network transfer costs when replicating data across regions by shrinking file sizes[7]. Platforms like SurferCloud provide tools to seamlessly manage both compression and lifecycle policies, helping you maximize storage efficiency with minimal effort.
Getting rid of unused data can lead to substantial savings. Orphaned data refers to storage resources - like unattached volumes - that continue to rack up charges even after their associated servers are no longer active. Unused data, on the other hand, includes outdated backups, duplicate files, or information that has outlived its retention period. Since cloud providers charge for all provisioned storage, whether or not it's being used, these forgotten resources can quietly drain your budget. Cleaning up these data assets works hand-in-hand with strategies like data tiering and compression to cut down on hidden storage costs.
The financial impact of orphaned resources can escalate quickly. For instance, a single unattached volume holding 100 GB costs about $0.10 per GB each month. While that might not seem like much, keeping 50 such volumes unnecessarily could cost you $500 per month - or $6,000 a year [9]. Sysco managed to cut its overall storage costs by over 40% by using automation to identify and eliminate over-provisioned resources continuously [4].
Most cloud providers offer tools to simplify cleanup tasks. For example, you can set lifecycle rules to automatically delete incomplete multipart uploads older than seven days, clearing out unnecessary file fragments [10]. Similarly, enabling Time To Live (TTL) features for databases and logs ensures that outdated data is automatically removed when it’s no longer relevant [15,18]. Tagging storage resources with labels like environment, owner, or application can help you quickly identify what can be deleted. Before removing an unattached volume, it’s wise to check its attachment history and create a final snapshot as a low-cost backup option [9].
Removing unused data doesn’t just save money - it can also improve system performance. With less irrelevant data to sift through, queries can run faster. Storage analysis tools can pinpoint "cold" buckets with zero retrieval activity and flag when outdated object versions are unnecessarily inflating your storage costs [10].
Manually cleaning up data becomes impractical as your storage needs grow. Automated solutions, such as lifecycle policies and snapshot management tools like Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager [16,18], can handle this task continuously with minimal effort. For organizations managing storage across multiple regions or accounts, monitoring dashboards can highlight the biggest opportunities for cleanup. Platforms like SurferCloud integrate lifecycle management tools with your workflows, making it easier to maintain organized and cost-efficient storage at any scale.
Smart storage classes take the guesswork out of managing data storage costs by automatically moving files to the most cost-effective tier based on their usage. Unlike manual tiering, this approach eliminates the need for setting up complex rules, making it especially useful when it's difficult to predict which files will be accessed often and which will stay dormant for months.
The financial benefits of smart storage classes are hard to ignore. Since its introduction in 2018, Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering has saved customers over $6 billion in storage costs [6]. Here’s how the savings break down:
Real-world examples highlight the impact. Torc Robotics saved 24% on monthly storage for petabytes of vehicle data, while Electronic Arts reduced data lake storage expenses by 30% [6].
"For every 1 TB of data, the company saves 60 percent on storage costs. I think it's the biggest return on investment that we've ever seen." – Al Maynard, Director of Software Engineering, Illumina [6]
These savings make a compelling case for adopting smart storage classes, and they’re paired with a simple implementation process.
Smart storage classes are built on a "set-it-and-forget-it" principle. Once activated, the system handles data tiering automatically - no need for manual analysis or complicated rule setups. Better yet, there are no extra retrieval fees to worry about [8].
A small monthly monitoring fee applies for tracking access patterns, but this only affects objects larger than 128 KB [4]. Smaller objects remain in the frequent access tier, so they won’t benefit from cost reductions [4].
"S3 Intelligent-Tiering was our 'easy' button and helped us move at the speed we needed without adding development cycles." – Justin Brown, Head of Vehicle Data Acquisition, Torc Robotics [6]
Smart storage classes are designed to keep pace with growing data needs, making them perfect for dynamic environments like new applications, data lakes, or analytics systems where usage patterns are still uncertain [8]. For even greater savings, you can manually enable Archive Access and Deep Archive Access tiers for data that can handle delayed retrieval [11].
When paired with lifecycle rules, smart storage classes can create a fully automated, scalable system that transitions data seamlessly from standard storage to lower-cost tiers as needed [11]. This combination ensures your storage solution grows with your business while keeping costs under control.
It's easy for businesses to overspend on storage by provisioning more than they actually need. This "just in case" approach often leads to unnecessary costs for unused storage, sometimes referred to as "ghost costs." The fix? Regularly adjust your storage volumes to match your actual data usage.
Right-sizing your storage can make a noticeable difference in your budget. For example, block storage typically costs around $0.10 per GB per month. A 1,000 GB volume would then cost $100 monthly[5]. But if you're only using 400 GB, you're wasting about $60 every month on unused capacity. The costs are even higher for managed databases - $2 per 10 GB per month for MySQL and PostgreSQL, or $0.20 per GB per month for MongoDB[5].
Modern cloud platforms make it easier to control these costs. They allow you to scale storage independently of compute resources, meaning you don’t need to upgrade CPU or RAM unnecessarily. You can add storage in increments as small as 10 GB, offering precise control over spending[5]. With managed databases, storage can scale up to 15 TB for MySQL/PostgreSQL or 16 TB for MongoDB, all without affecting your compute tier[5].
Adjusting storage volumes has become incredibly straightforward with today's cloud tools. Through user-friendly control panels or APIs, you can increase disk space with just a few clicks. For those who prefer automation, tools like Terraform or command-line interfaces make the process even smoother[5]. You can also set up alerts to expand storage automatically when you're nearing capacity.
"Increase disk storage via the cloud console or API - a simple and intuitive way to adjust storage to meet business needs." – DigitalOcean[5]
While expanding storage is easy, shrinking it can be more challenging. It often requires migrating data to a smaller volume, which takes time and planning. That's why continuous monitoring is key. By identifying underutilized volumes, you can consolidate data onto smaller, more cost-effective storage options.
Automation can turn storage management into a hands-off process. Start new workloads with only the minimum required storage and use APIs to automatically expand capacity as demand grows[5]. This ensures you’re only paying for the storage you actually use.
"With well-managed storage, you can scale up or down based on your usage needs. This prevents performance bottlenecks and aligns infrastructure usage with business growth." – DigitalOcean[5]
To maximize efficiency, combine monitoring tools with automated scaling policies. Set rules to add storage in small increments as needed, and regularly audit your system to remove unattached or underutilized volumes[12]. This approach creates a lean, responsive storage setup that keeps costs under control while meeting your business's needs.
At SurferCloud, we make this process even easier. Our intuitive control panel and powerful APIs let you adjust storage volumes effortlessly, ensuring you only pay for the capacity you actually use.
Reducing cloud storage costs is achievable with a mix of data tiering, compression, removing orphaned data, smart storage classes, and right-sizing volumes. When executed together, these strategies can lead to substantial savings. For instance, data compression can lower storage needs by up to 75% [3], and archiving inactive data can cut costs by over 80% [3]. By layering these approaches, businesses can eliminate wasteful spending and maximize efficiency.
"Cloud storage can be dirt-cheap, but only if you approach it intelligently. Choose an optimal cloud platform, storage services, and data management strategies to keep your cloud storage costs as low as possible." - Christopher Tozzi, Technology Analyst [2]
However, cost optimization in the cloud isn’t a one-and-done task - it’s an ongoing effort. Research shows that companies waste about 30% of their cloud budgets, with 78% of organizations estimating that 21–50% of their annual cloud spend goes to idle or over-provisioned resources [13][14]. This is where a provider like SurferCloud can make a difference. With 17+ global data centers spread across four continents, elastic scaling options, and 24/7 expert support, SurferCloud empowers businesses to fine-tune their storage setups without being locked into a single vendor [1].
To sustain these savings, continuous monitoring and agile resource management are key. SurferCloud's intuitive tools and global infrastructure simplify these tasks, ensuring that businesses pay only for the resources they actually use - whether scaling up during busy periods or consolidating underutilized assets.
Data tiering is a smart way to cut costs by sorting your data into various storage levels based on how often it's accessed. Hot data - the stuff you use all the time - stays in high-performance (and more expensive) storage. Meanwhile, cold data, which you rarely touch, is automatically shifted to more budget-friendly storage options.
This method allows you to reserve premium storage for what truly matters, while less critical data is stored at a lower cost. The result? Businesses can trim their cloud expenses without compromising on performance or access when they need it.
Smart storage classes take the hassle out of managing data by automatically shifting files between storage tiers based on how they're being used in real time. This means your data is always stored in the most cost-efficient tier without sacrificing performance. No more manual adjustments or worrying about overspending on storage.
What’s even better? There are no retrieval fees, and frequently accessed files are automatically moved to faster tiers. This makes smart storage classes an ideal choice for workloads with unpredictable access patterns, such as data lakes or analytics pipelines. With SurferCloud’s smart storage solutions, businesses across the U.S. can trim down storage expenses while ensuring their data is always accessible when they need it.
Data compression works by encoding files in a way that reduces their size, allowing them to take up less storage space. This not only cuts down on storage costs but can also help lower related expenses, like data transfer and scanning fees.
Smaller files mean businesses can maximize their existing storage capacity, avoiding the need for expensive upgrades or buying extra storage. Compression offers a smart way to manage cloud storage costs while keeping data accessible and maintaining performance.

Managing multi-cloud environments is complex. From inco...
In the world of cloud computing and virtualization, Vir...
In the high-stakes world of scientific research, "Compu...