Which Hosting Company Has a Friendly Technica
Choosing a hosting company is more than just comparing ...







Horizontal scaling means adding more servers to handle increased traffic instead of upgrading a single machine. This approach improves performance during traffic spikes, provides redundancy, and supports growth. Auto scaling automates this process by adjusting resources in real time based on demand, saving costs and effort.
Key highlights:
Auto scaling ensures steady performance, reduces waste, and keeps costs low by scaling resources up or down based on real-time needs or predictions.
SurferCloud offers a robust auto scaling system powered by elastic compute servers that adapt resources in real time. Here's how these solutions enhance both performance and cost management.
SurferCloud's elastic compute servers keep an eye on workloads around the clock, instantly adding capacity during traffic surges to maintain reliable application performance. When traffic slows, resources automatically scale down, cutting unnecessary costs. This adaptive approach ensures a balance between performance and affordability, catering to businesses of all sizes.
With over 17 data centers strategically located worldwide, SurferCloud ensures scaling happens close to your users, minimizing delays. By distributing resources across regions, it maintains high availability - even during zone failures - while predictive scaling allocates resources ahead of expected spikes, reducing latency issues [8][2][3][5]. Plus, regular health checks automatically replace underperforming servers to keep operations smooth.
SurferCloud provides 24/7 expert support to help businesses transition from manual to automated scaling. Their team assists in setting up event-based scaling triggered by metrics like request volume or server queues. They also guide businesses in configuring scheduled scaling for predictable events, such as Black Friday sales or major product launches [9].
Various cloud platforms and orchestration systems offer specialized tools to manage horizontal scaling. Knowing how these tools work can help you make the right choice for your infrastructure.
The Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) automatically adjusts the number of Pods in a Deployment, StatefulSet, or ReplicaSet based on resource demand [6][12]. It evaluates metrics every 15 seconds and supports scaling based on built-in metrics like CPU and memory usage, custom metrics such as requests per second, and external metrics like message queue length [6][10]. If multiple metrics are configured, HPA uses the highest recommended replica count to maintain performance.
To avoid rapid fluctuations, HPA includes a 5-minute stabilization period for scaling down and ignores metric changes within a 10% tolerance range [6][10]. Properly defining CPU and memory requests in your Pod specifications is key for accurate scaling decisions. While HPA itself is free, you’ll incur charges for the cloud resources used by additional Pods [11][3].
AWS Auto Scaling offers a unified solution for scaling various resources like EC2 instances, Spot Fleets, ECS tasks, DynamoDB tables, and Aurora Replicas [2][3]. It combines real-time dynamic scaling, driven by CloudWatch alarms, with predictive scaling that uses machine learning to forecast demand and pre-provision capacity [3][4].
Target tracking policies help maintain specific metrics, such as keeping CPU utilization at a desired percentage, while health checks automatically replace unhealthy EC2 instances to ensure availability. AWS Auto Scaling itself has no additional cost; you only pay for the resources you use and standard CloudWatch monitoring fees [7].
Google Cloud Auto Scaling adjusts capacity for workloads running in Compute Engine and Kubernetes Engine. It scales resources based on CPU, HTTP load, or custom metrics. You can also configure minimum and maximum instance counts to balance cost control with performance.
Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS) enable horizontal scaling of identical virtual machines using Azure Monitor Autoscale. Scaling actions are triggered by runtime metrics, schedules, or custom metrics [14][15]. The service also replaces unhealthy instances automatically and can use machine learning to predict demand and scale resources 15–60 minutes in advance [13][16].
In 2025, Victoria's Secret & Co. utilized Azure Kubernetes Service, which integrates VMSS for node scaling, achieving a threefold performance boost with 99.99% availability [17]. Kamal Abhinay, Head of Engineering & Architecture at Victoria's Secret & Co., shared:
"Azure just made sense for us. Choosing Azure Kubernetes Service not only provides us with the support and managed control plane, but also allows us to use most Kubernetes components as they are with fewer proprietary abstractions." [17]
Azure prioritizes scaling out over scaling in when rules conflict, ensuring uninterrupted service. To avoid frequent instance changes, it’s recommended to set clear margins between thresholds, such as scaling out at 80% CPU utilization and scaling in at 60% [14][15].
Next, we’ll compare the features and costs of these tools to highlight their specific strengths.
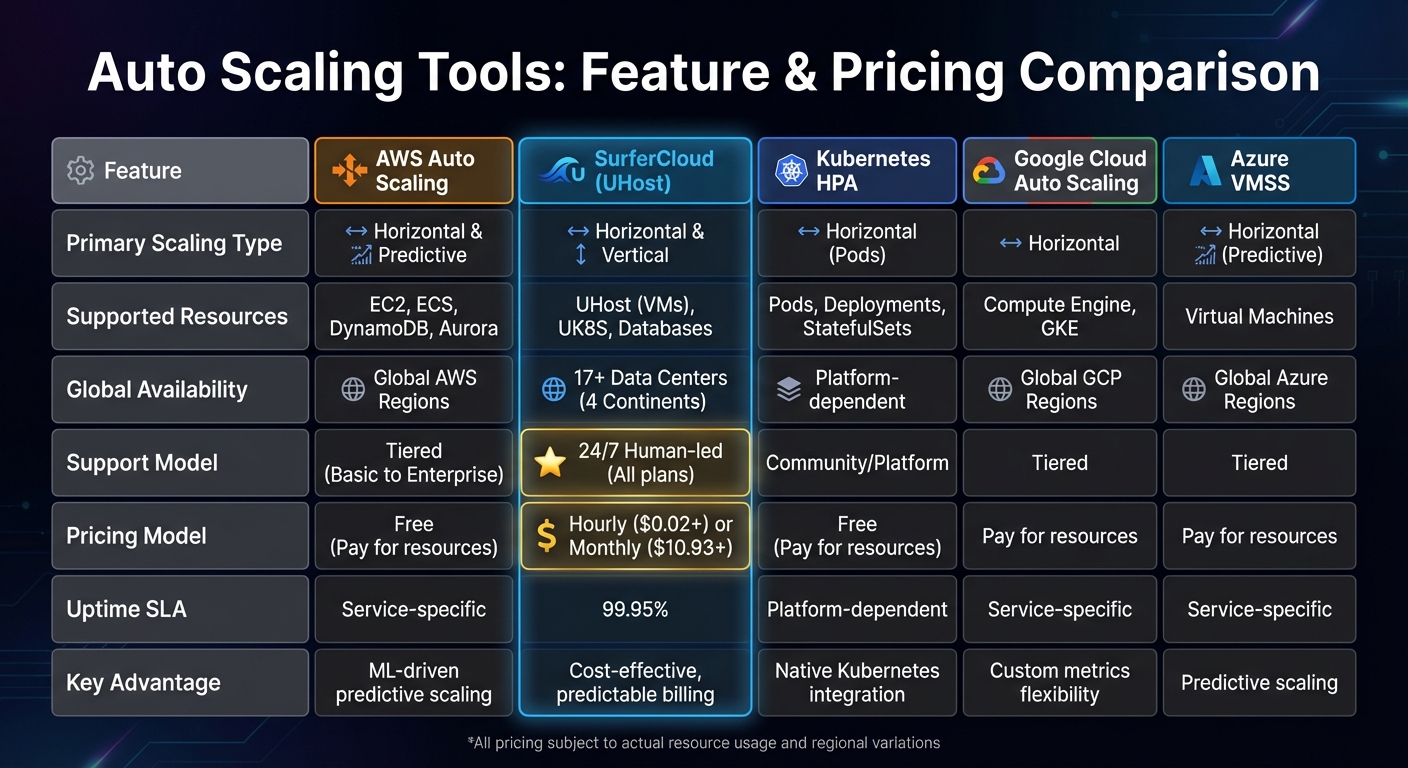
Auto Scaling Tools Comparison: AWS vs SurferCloud vs Kubernetes vs Google Cloud vs Azure
Selecting the right auto-scaling tool means weighing features, pricing, and the kind of support you’ll need. Below is a table that breaks down the key features and pricing for some of the most popular options.
| Feature | AWS Auto Scaling | SurferCloud (UHost) | Kubernetes HPA | Google Cloud Auto Scaling | Azure VMSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Scaling Type | Horizontal & Predictive | Horizontal & Vertical | Horizontal (Pods) | Horizontal | Horizontal (Predictive) |
| Supported Resources | EC2, ECS, DynamoDB, Aurora | UHost (VMs), UK8S, Databases | Pods, Deployments, StatefulSets | Compute Engine, GKE | Virtual Machines |
| Global Availability | Global AWS Regions | 17+ Data Centers (4 Continents) | Platform-dependent | Global GCP Regions | Global Azure Regions |
| Support Model | Tiered (Basic to Enterprise) | 24/7 Human-led (All plans) | Community/Platform | Tiered | Tiered |
| Pricing Model | Free (Pay for resources) | Hourly ($0.02+) or Monthly ($10.93+) | Free (Pay for resources) | Pay for resources | Pay for resources |
| Uptime SLA | Service-specific | 99.95% | Platform-dependent | Service-specific | Service-specific |
| Key Advantage | ML-driven predictive scaling | Cost-effective, predictable billing | Native Kubernetes integration | Custom metrics flexibility | Predictive scaling |
SurferCloud stands out with its transparent and predictable pricing, starting at just $0.02 per hour or $10.93 per month. Unlike some competitors, its pricing remains consistent throughout your subscription. Plus, UHost plans include unlimited traffic, so you won’t have to worry about overage charges [19][18].
Every SurferCloud plan includes 24/7 human-led support, giving you access to a team of experts for performance tuning and cloud consulting. Their team consists of specialists from leading cloud providers, ensuring professional guidance at all times [19][18].
Another perk? SurferCloud takes care of Windows licensing costs and offers flexible payment options, including credit cards, PayPal, and even cryptocurrencies. No mandatory KYC is required, making payments hassle-free [19][1].
With 17+ global data centers across four continents, SurferCloud delivers low-latency scaling for distributed workloads. The platform integrates seamlessly with VPC, UK8S, load balancing, and US3 object storage, making it a solid choice for modern cloud-native setups. Backed by a 99.95% availability guarantee, it offers the reliability enterprises need [19][18][1].
To manage horizontal scaling effectively, start by defining clear capacity boundaries for your auto scaling group. This means setting minimum, maximum, and desired capacity levels to balance performance needs and budget constraints. The minimum capacity ensures you always have enough resources for baseline operations, while the maximum capacity prevents runaway costs during unexpected traffic surges [20][8].
For most workloads, target tracking policies are a reliable choice. Think of them as a thermostat - they automatically adjust capacity to maintain a specific metric, like keeping average CPU utilization at 50% [20][22]. If you need more control, step scaling allows you to adjust capacity in fixed increments when certain thresholds are crossed [20][21]. For predictable traffic patterns, scheduled scaling can be used to adjust capacity at predefined dates and times [23].
When selecting metrics, focus on those that inversely correlate with capacity. For instance, doubling the number of instances should roughly halve the average CPU utilization [20][22]. Common metrics include CPU utilization, network I/O, and load balancer request counts. Be sure to configure instance warmup times to ensure new instances are fully operational before they impact overall performance metrics [21][22].
Keep refining your scaling strategy by continuously monitoring and analyzing these metrics.
Once your scaling policies are in place, the next step is to monitor performance metrics closely. For example, Kubernetes HorizontalPodAutoscaler checks resource utilization every 15 seconds by default [6], while AWS CloudWatch typically updates metrics every 5 minutes [6][22]. If faster responses are required, enabling detailed monitoring in CloudWatch can provide data at 1-minute intervals, allowing your autoscaler to react more quickly to sudden traffic spikes [22].
When monitoring, avoid total metrics like overall request counts or latency, as they may not scale proportionally with additional instances [22]. Instead, focus on resource-specific metrics such as CPU and memory usage for standard web servers. For specialized applications, custom metrics like "packets-per-second" may be more relevant. In message processing workloads, metrics like SQS queue length can serve as early indicators, helping you scale before instances become overwhelmed [6][22].
To ensure high availability during horizontal scaling, distribute instances across multiple availability zones. This approach safeguards your application against zone failures, ensuring it remains online [8][24]. Auto scaling tools can automatically balance capacity across these zones and replace unhealthy instances through health checks [8][4].
For faster response times during sudden traffic spikes, consider using warm pools. These pre-initialized instances reduce the time it takes to scale out [8]. Additionally, launch templates can help you specify multiple instance types and purchase options - such as a mix of On-Demand and Spot instances - to maintain capacity even if certain instance types are unavailable [8]. When multiple scaling policies are active, the system prioritizes the one that offers the largest capacity increase, helping to avoid premature scale-ins during traffic surges [20].
Horizontal scaling plays a key role in cloud infrastructure by adjusting capacity based on demand, ensuring both efficiency and cost management. As explained earlier, striking the right balance in scaling strategies is essential in modern cloud environments.
The key to success lies in blending different scaling approaches. Predictive scaling leverages machine learning to anticipate traffic patterns and allocate resources ahead of time. On the other hand, dynamic scaling reacts to real-time metrics, such as CPU usage or incoming request volumes. Among these, target tracking policies stand out - they adapt over time by learning actual workload patterns, reducing capacity swings and improving performance consistency [3]. These strategies pave the way for solutions like those offered by SurferCloud, which integrate dynamic scaling effortlessly.
SurferCloud provides a robust solution for achieving low-latency, high-availability scaling. Most auto-scaling tools, including theirs, operate on a pay-as-you-go pricing model. This means businesses only pay for the compute and monitoring resources they actually use, making it a budget-friendly option [2][7]. This flexible pricing approach allows companies to start small and scale up as their needs grow, without the burden of upfront costs or complicated licensing.
Auto scaling is a smart way to control costs by adjusting resources in real time to match demand. When traffic spikes, it adds extra capacity to ensure your system can handle the load. And when things slow down, it reduces resources to cut down on unnecessary expenses. This approach means you're only paying for what you actually use, striking a balance between cost efficiency and maintaining reliable performance.
Elastic compute servers offer a flexible, on-demand way to scale cloud applications by automatically adjusting computing power as workloads shift. This adaptability makes them perfect for managing unpredictable traffic while keeping performance high and costs under control.
Here’s why they stand out:
With these advantages, businesses can focus on delivering seamless, high-quality user experiences and driving growth, rather than getting bogged down in infrastructure concerns.
Predictive scaling and dynamic scaling tackle workload fluctuations in distinct ways. Predictive scaling uses historical data - like daily or weekly traffic trends - to anticipate future demand and adjust capacity ahead of time. This method is particularly effective for workloads with regular patterns, such as business hours or scheduled batch processing, as it helps prevent delays and avoids over-provisioning.
Dynamic scaling, in contrast, responds to real-time metrics like CPU usage or request rates, adjusting resources as demand shifts. This makes it a great fit for handling unpredictable traffic spikes. However, since adjustments happen after demand increases, there may be a slight delay in scaling.
By combining these two strategies, you can create a more efficient and cost-conscious approach to horizontal scaling.
Choosing a hosting company is more than just comparing ...
When it comes to reliable, secure, and high-performance...
6 Tbps DDoS Attack Hits Hosting Provider — Why VPS Bu...