What Are the Best Cloud Server Providers in T
Why Cost and Scale Matter in Cloud Hosting Cloud hos...







Serverless AI training with TensorFlow eliminates the need to manage infrastructure, allowing you to focus on developing and training models. By leveraging serverless platforms, you can scale resources automatically, pay only for the compute time used, and simplify the deployment process. TensorFlow's prebuilt Docker images and tools make it easy to transition from local development to serverless environments for tasks like distributed training and inference.
Serverless platforms like SurferCloud simplify AI training by automating resource provisioning, offering flexible compute options (CPUs, GPUs, TPUs), and supporting large-scale training with minimal setup. Whether you're experimenting with models or scaling for production, serverless infrastructure provides a streamlined, efficient solution.
Before jumping into serverless AI training with TensorFlow, it’s essential to prepare your development environment and gather the necessary tools.
To get started, make sure you’re using Python 3.6 or later, which is compatible with TensorFlow cloud training [5][6]. Install TensorFlow, which includes the high-level API tf.keras for building and training neural networks. You’ll also need Docker Engine to package your training applications into container images [5][2].
For cloud resources, a SurferCloud account is key. It provides access to scalable compute resources like GPUs/TPUs and robust storage capabilities [1][2]. The Serverless Framework and its command-line interface will help you authenticate your account, manage resources, and trigger training jobs [5][2]. Don’t forget to set up cloud storage for datasets, Python libraries, and model artifacts. Additionally, include libraries like numpy, matplotlib, and grpcio for tasks such as data manipulation, visualization, and API communication [1][2][6].
Once these tools are in place, it’s time to dive deeper into TensorFlow’s model-building and training features.
Familiarize yourself with tf.keras to construct a Sequential model using layers like Conv2D, Flatten, and Dense. Compile the model with the Adam optimizer and SparseCategoricalCrossentropy for loss calculation, and save your trained model using the SavedModel format [6].
Preprocessing your data is a crucial step. Normalize input values (e.g., scale pixel values between 0.0 and 1.0) and reshape the data into tensors that align with your model’s input specifications. Use the saved_model_cli utility to inspect your model’s SignatureDefs, which define its input and output formats, before deploying [6].
With these basics covered, you’ll be ready to set up the cloud infrastructure to scale your training jobs.
After setting up TensorFlow locally, the next step is to configure SurferCloud resources for large-scale training. Start by defining worker pools that specify machine types (CPUs), memory requirements, and bandwidth [1][4]. For resource-intensive TensorFlow tasks, opt for GPUs or TPUs to accelerate training [1][2]. Choose boot disks based on your workload - standard sizes start at 100 GiB, but you can scale up to 64,000 GiB. If your application involves frequent data reads and writes, SSDs are a better choice than HDDs for faster performance [1][2].
To ensure secure and efficient operations, enable VPC peering and configure IAM roles for controlled access [1][4]. Link your compute resources to relevant data sources, such as Cloud Storage buckets, BigQuery, or NFS shares, for seamless access to training datasets. With SurferCloud's serverless infrastructure, resources are provisioned only when needed and automatically decommissioned after the training job is complete, helping you manage costs effectively [1][7].
Before deploying your TensorFlow model, it's crucial to build and train it locally. This step ensures the model works as expected before scaling up with SurferCloud's serverless infrastructure.
Start by defining your neural network using tf.keras.Sequential, which allows you to stack layers easily. For tasks like image classification, a typical architecture includes:
If you're working with grayscale images, set the input shape to (28, 28, 1). Normalize pixel values by dividing them by 255.0 [6] [8].
When compiling the model, use the Adam optimizer and SparseCategoricalCrossentropy as the loss function. If your Dense output layer doesn't include softmax activation, make sure to set from_logits=True in the loss configuration [6] [8]. A basic neural network trained on the MNIST dataset can achieve about 98% accuracy in just 5 epochs [8].
Use model.fit to run your training loop locally. This step ensures the model converges properly before transitioning to cloud-based training. Train on a representative dataset and monitor metrics like loss and accuracy to confirm the model's performance. By validating locally, you avoid unnecessary use of cloud resources.
For subclassed models, it's important to "trace" the model by calling it at least once or running model.fit before saving it. Without this step, model.save may fail to create the required ConcreteFunction objects [9]. Establishing a strong baseline locally ensures you have a reliable point of comparison when scaling up in a serverless environment.
Once you're satisfied with the results, it's time to save your model artifacts.
After completing training, save your model in the SavedModel format using tf.keras.models.save_model. This format generates a directory containing the saved_model.pb file (which stores the model architecture) and a variables/ folder (which holds the trained weights) [6]. The SavedModel format is essential for smooth deployment on SurferCloud.
For better version management, store exports in versioned subdirectories like /model_path/1/ or /model_path/2/. This structure allows serverless tools like TensorFlow Serving to handle multiple versions efficiently [6].
"If you use TensorFlow to train a model, export your model as a TensorFlow SavedModel directory." - Google Cloud Documentation [11]
To verify the export, use the command saved_model_cli show --dir {export_path} --all. This shows the SignatureDefs and confirms the input and output tensor names required for deployment [6]. The serving_default key specifies the inference function that serverless platforms will utilize [9].
If your training occurred on remote accelerators but you need to save the model locally, use tf.saved_model.SaveOptions(experimental_io_device='/job:localhost') to ensure the artifacts are written to your local disk correctly [9].
Once the export is verified, you’re ready to deploy the model artifacts to SurferCloud’s serverless environment.
Once your model is exported, the next step is deploying it to SurferCloud's serverless environment. This involves transferring your model files, setting up serverless functions, and ensuring your deployment is secure.
TensorFlow models often exceed serverless package size limits (50 MB compressed, 250 MB uncompressed) [12]. To accommodate this, store your SavedModel directory in SurferCloud's cloud storage.
Use the SurferCloud CLI to handle the upload process. Start by initializing your storage bucket and then upload your model directory using recursive copy commands. For example, if your model is located at /local/model/1/, upload it while keeping its versioned structure intact. During cold starts, serverless functions will download these artifacts to the /tmp directory.
Organize models in versioned paths like /models/tensorflow/v1/ or /models/tensorflow/v2/. This structure simplifies tasks like rollbacks and A/B testing [12].
Your serverless function should focus on handling inference requests, as serverless setups lack the resources needed for model training [14]. The function code must load the TensorFlow model from SurferCloud storage into the /tmp directory during cold starts and then process incoming prediction requests.
For inference-only workloads, consider using the lightweight tflite-runtime [12]. Alternatively, SurferCloud's layer functionality can help separate TensorFlow dependencies from your main application code.
Be prepared for some latency: cold starts typically take 4.5–10 seconds, while warm invocations average about 3 seconds [13]. For applications with high traffic, provisioned concurrency can help keep functions warm, minimizing delays.
In terms of cost, deploying TensorFlow in a serverless environment is economical, with an estimated $1 per 25,000 requests [13]. After optimizing your functions for performance, focus on securing the deployment to protect your data and operations.
To enhance security, use VPC endpoints or VPC peering for private communication between your serverless functions and model storage [1]. This prevents exposure to public internet routes and keeps data within a secure network.
Assign IAM roles with the least privilege necessary, ensuring functions can only access designated storage buckets [1]. Use an API Gateway as the front end for your functions to manage authentication, rate limiting, and CORS headers [15]. For accessing model artifacts, avoid public URLs; instead, rely on signed URLs or private VPC endpoints [14].
Encryption is critical for meeting compliance standards. Protect data both at rest and in transit, and take advantage of SurferCloud's support for customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK) to address specific regulatory needs [1]. A secure serverless setup should also include access control mechanisms, audit trails, and compliance with privacy regulations [16].
With proper networking and security measures in place, SurferCloud’s serverless architecture can handle up to 10,000 concurrent requests without requiring additional configuration [13]. This scalability ensures that your deployment remains both secure and efficient.
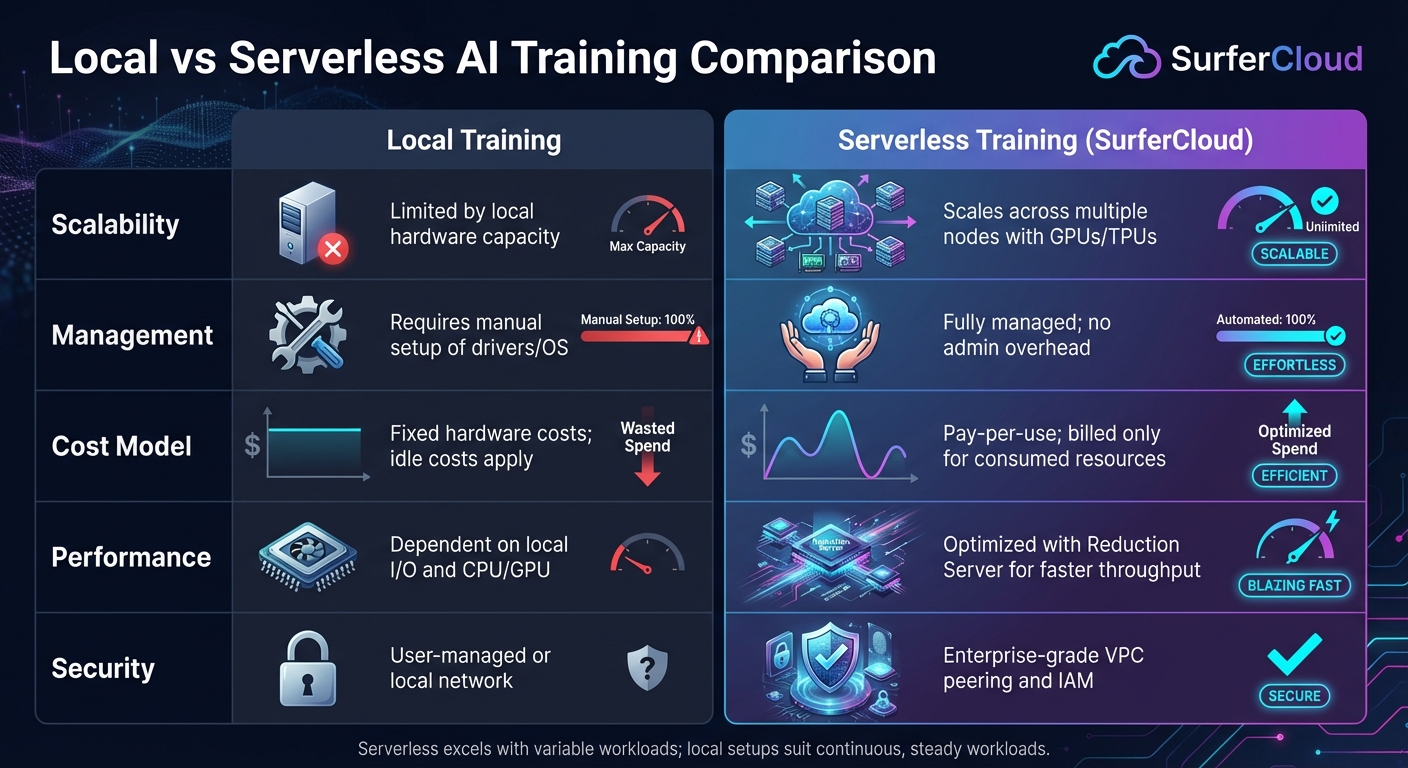
Local vs Serverless AI Training: Performance and Cost Comparison
Getting the best performance out of your model in a serverless setup means tackling several aspects: compute resources, network settings, and the model's architecture. Start by choosing the right machine types for your workload. Adding GPUs or TPUs can significantly speed up training, and switching to SSD boot disks can enhance I/O performance for faster data handling [1][2].
For distributed training with NVIDIA GPUs, using an all-reduce algorithm can improve throughput and reduce latency across nodes [1][3]. To ensure secure and efficient communication between your serverless functions and data sources, configure VPC Network Peering. This keeps traffic within private networks, minimizing latency and enhancing security [1][4]. Additionally, automated hyperparameter tuning can save time and effort by finding the best configurations to boost your model's accuracy without manual trial-and-error [1]. Once these optimizations are in place, monitoring tools are essential to ensure everything runs smoothly.
After optimizing performance, keeping an eye on metrics and logs is critical to verifying those improvements. One useful tool here is Cloud Profiler. By installing and initializing the google-cloud-aiplatform[cloud_profiler] plugin at the start of your code with cloud_profiler.init(), you can monitor CPU, GPU, and memory usage to identify bottlenecks in your training operations [17][18]. Keep in mind that Cloud Profiler requires TensorFlow version 2.4 or later [18].
To track training progress in real time, set the AIP_TENSORBOARD_LOG_DIR environment variable. This automatically syncs training logs to TensorBoard, where you can visualize metrics like accuracy, loss, and weight histograms [17][18]. While your training job runs, capture profiling sessions in TensorBoard's 'Profile' tab using your worker pool identifier (e.g., workerpool0-0) [18]. For a centralized view, SurferCloud’s console provides access to job statuses, logs, and error messages, making it easier to troubleshoot and monitor [10][17].
Comparing metrics between local and serverless training environments can highlight the strengths and limitations of each approach. This helps you make informed decisions about your infrastructure. Here’s a quick breakdown:
| Metric | Local Training | Serverless Training (SurferCloud) |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Limited by local hardware capacity | Scales across multiple nodes with GPUs/TPUs [1] |
| Management | Requires manual setup of drivers/OS | Fully managed; no admin overhead [1] |
| Cost Model | Fixed hardware costs; idle costs apply | Pay-per-use; billed only for consumed resources [1] |
| Performance | Dependent on local I/O and CPU/GPU | Optimized with Reduction Server for faster throughput [1] |
| Security | User-managed or local network | Includes enterprise-grade VPC peering and IAM [1] |
Serverless training shines when dealing with variable workloads, offering scalability and reduced maintenance. On the other hand, local setups might be more predictable in terms of costs for continuous, steady workloads. Each approach has its place, depending on your specific needs and constraints.
Serverless AI training with TensorFlow simplifies the process of building models by removing the need to manage infrastructure. With auto-provisioning of compute resources, you only pay for the time you actually use, avoiding the idle costs typically associated with traditional setups [1]. The platform scales effortlessly - whether you're working on small prototypes or running distributed training across multiple nodes powered by GPUs and TPUs. It also includes features like automated hyperparameter tuning and advanced all-reduce algorithms that improve communication efficiency in multi-node setups. Plus, enterprise-level security measures, such as VPC peering and customer-managed encryption keys, ensure your data and models are protected [1].
Ready to take advantage of these benefits? Start by creating your SurferCloud account and running a basic single-node training job to get familiar with the workflow [2][4]. SurferCloud offers prebuilt TensorFlow containers with commonly used dependencies, so you can focus on refining your model instead of dealing with configuration challenges. Once you're comfortable, try the autopackaging feature, which allows you to push your local code to the cloud with a single command - making the transition from development to production seamless. As your projects grow, you can expand into distributed training to handle larger datasets. And with expert support available 24/7, you'll have the guidance you need to scale your AI training operations with confidence.
Using TensorFlow for serverless AI training comes with several advantages that make the process smoother and more efficient:
By removing operational complexities, this approach lets you spend more time improving your AI models and achieving stronger outcomes.
To get started with serverless TensorFlow training on SurferCloud, you'll need to set up your environment properly. Begin by installing Python 3.6 or newer and confirm the installation by running python --version. After that, install the Google Cloud CLI (gcloud), log in to your SurferCloud account, and set your project ID. You'll also need to enable the necessary AI services for your project using this command: gcloud services enable aiplatform.googleapis.com.
If you plan to build a training container locally, make sure to install Docker. Alternatively, you can create a Cloud Storage bucket to store your training code. Package your TensorFlow training code into a .tar.gz or .whl file and upload it to the bucket using the gsutil cp command. When you're ready, submit a serverless training job through the CLI, detailing the training configuration. This includes specifying the machine type, container image, and Python module.
With this setup in place, you can concentrate on developing your AI models while SurferCloud takes care of the infrastructure in the background.
SurferCloud prioritizes security in serverless AI training by leveraging isolated infrastructure. Every training job operates within its own dedicated, sandboxed container, ensuring there’s no risk of data mixing or leaks between tenants. Plus, your data and model artifacts remain confined to your chosen cloud region unless you explicitly decide otherwise.
To strengthen this protection, SurferCloud employs enterprise-level security features like encrypted storage, network firewalls, and role-based access controls. From the moment you upload data to the point where your trained model is stored or exported, these measures safeguard your AI workflows, letting you focus on innovation without worrying about security risks.

Why Cost and Scale Matter in Cloud Hosting Cloud hos...
What is the difference between VPS and cloud server? Wh...
When it comes to Forex trading, having a reliable and f...