Host an IRC or Discord Relay Node on SurferCl
? Pain Point Running chat relays between IRC, D...






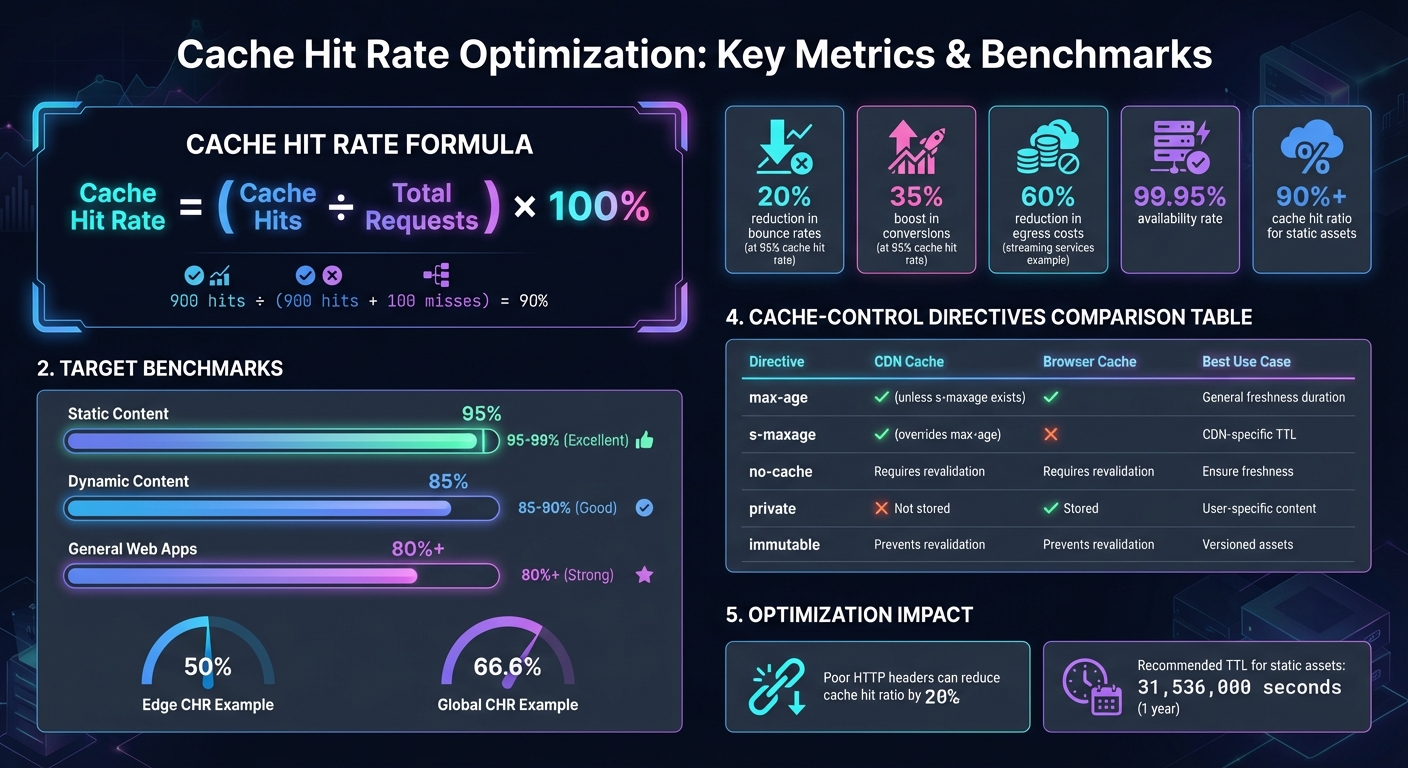
Want faster website performance and lower costs? Start by improving your cache hit rate. A high cache hit rate ensures most user requests are served from edge servers rather than slower origin servers. This reduces latency, improves user experience, and saves bandwidth costs. For instance, a 95% cache hit rate can reduce bounce rates by 20% and boost conversions by 35%.
Here’s the gist:
This guide covers practical strategies, from setting Cache-Control headers to advanced methods like origin shielding and cache warming, to help you optimize your cache and improve performance.
Cache Hit Rate Optimization: Key Metrics and Performance Benchmarks
To calculate your cache hit rate, divide the number of cache hits by the total number of requests (cache hits plus misses). For example, if your CDN serves 900 requests from the cache and pulls 100 from the origin, your cache hit rate would be 90% [4].
Some advanced setups break this down further into local Edge Cache Hit Rate (Edge CHR) and overall Global Cache Hit Rate (Global CHR) [10]. For instance, Fastly reported an Edge CHR of 50%, while their Global CHR, which also includes shield hits, was 66.6% [10].
It's a good practice to calculate these metrics on an hourly, daily, or weekly basis. This allows you to monitor trends and assess how changes in configuration affect performance [1][9]. For an even more precise measure, some approaches exclude "Pass" requests - like API calls that aren’t cacheable - from the calculation [10].
For websites with mostly static content, a cache hit rate between 95% and 99% is considered excellent [1][8][10]. In general, a hit rate above 80% is seen as strong for most web applications [9].
However, the ideal rate depends on your specific content. Websites with predominantly static assets aim for 95–99%, while those serving dynamic content often target a slightly lower range, around 85–90% [4][10].
Several factors can negatively impact your cache hit rate, including URL inconsistencies, query string variations, and limited cache storage [2][10]. For example, if your CDN treats /home and /home/ as separate resources, or if tracking parameters like utm_source create multiple cache entries, your hit rate will drop [2][4].
Cache storage capacity is another key element. Limited space can lead to frequent object evictions, often managed by algorithms like Least Recently Used (LRU) or Least Frequently Used (LFU). High eviction rates directly reduce your hit rate [10][5]. Similarly, after deployments or cache purges, a "cold cache" must refill from the origin, causing temporary dips in performance [7][5].
First-time visitors also contribute to lower hit rates, as they lack a local browser cache, resulting in an initial 0% hit rate for those users [7]. Additionally, poorly configured HTTP headers can slash your cache hit ratio by as much as 20% [4]. By understanding these factors, you can prioritize optimization efforts where they’ll make the biggest difference.
These insights provide a foundation for the next steps: strategies to improve your cache hit rate.
Setting proper Cache-Control headers is one of the quickest ways to improve your cache hit rate. For static assets with versioned filenames (like style.x234dff.css), you can safely set max-age to 31,536,000 seconds (one year) [12][14]. These files don’t change, so caching them for an extended period poses no risk.
For better control, use s-maxage to specify caching duration at the edge (e.g., your CDN), while keeping a shorter max-age for browsers [11][13]. For instance, you could set s-maxage=3600 for your CDN and max-age=300 for browsers.
The stale-while-revalidate directive is another useful tool. It allows outdated content to be served while a fresh version is fetched in the background [11][2]. Similarly, stale-if-error ensures availability during server issues by serving stale content when your origin server returns 500-level errors [11][2].
For assets that don’t change (like cache-busted files), add the immutable directive. This stops browsers from revalidating the content, even when users refresh the page [11]. On the other hand, avoid directives like private or no-store for public content, as they prevent CDN caching [11][13].
| Directive | Shared Cache (CDN) | Private Cache (Browser) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
max-age |
Respected unless s-maxage exists |
Respected | Sets general freshness duration |
s-maxage |
Overrides max-age for CDN |
Ignored | CDN-specific time-to-live (TTL) |
no-cache |
Requires revalidation | Requires revalidation | Ensures freshness without disabling storage |
private |
Not stored | Stored | For user-specific content |
immutable |
Prevents revalidation | Prevents revalidation | Ideal for unchanging, versioned assets |
Once your Cache-Control headers are configured, the next step is to fine-tune your cache key settings.
Cache keys determine whether a request results in a hit or a miss. For a cache hit to occur, the cache key for a new request must match an existing one exactly [16]. Simplifying your cache key increases the likelihood of hits [16].
Start by normalizing query strings and enforcing consistent casing. Exclude unnecessary tracking parameters like utm_source or fbclid [18][15]. Configure your CDN to forward only the query parameters that genuinely affect content, and ensure they’re always sent in the same order.
Avoid including high-cardinality headers like User-Agent in your cache key. Instead, use normalized headers such as CloudFront-Is-Mobile-Viewer to group requests by device type [2]. For cookies, forward only essential ones - never include unique session or user IDs in cache keys for static content, as this creates a separate cache entry for every user, negating the benefits of caching [2][17].
Normalize the Accept-Encoding header to prevent multiple cache entries for different encoding types [17]. Additionally, create distinct cache behaviors for static and dynamic content. For example, disable cookie-based caching entirely for files like *.css and *.js [2].
By combining these practices with content versioning and proactive cache warming, you can significantly enhance your cache performance.
Content versioning is a powerful way to avoid stale content issues and improve cache efficiency. Adding a hash to filenames - like app.9f1c2.js - ensures that any file update results in a new filename. This allows you to confidently set a long TTL (max-age=31,536,000) because caches will treat updated files as entirely new resources [19][20].
Pair versioning with the immutable directive using Cache-Control: public, max-age=31536000, immutable. This tells browsers not to revalidate the file until the TTL expires [19]. For HTML files referencing these assets, use shorter TTLs with background revalidation, such as public, s-maxage=60, max-age=0, stale-while-revalidate=300 [19][20].
"When you deploy a new version, the filename changes and caches naturally fetch the new asset." - CDNHandbook [19]
Cache warming complements versioning by preloading frequently accessed content into the cache after deployment. This reduces cache misses for newly deployed files and ensures a smoother user experience. Together, these strategies can help maintain a high cache hit rate and improve performance.
Cache shielding acts as a protective layer between edge servers and the origin, streamlining requests and safeguarding your infrastructure. Typically, when edge servers in different regions encounter cache misses for the same content, they each send separate requests to the origin. Cache shielding changes this dynamic by routing all these requests through an intermediary cache - commonly referred to as an "Origin Shield." This shield checks if the content is available before forwarding the request to the origin server [21][2].
This setup significantly reduces redundant requests. For instance, if multiple edge servers simultaneously miss the same file, the shield consolidates these requests so that only one reaches the origin.
"By offloading the origin and efficiently managing content requests, cache shielding ensures uninterrupted service during these critical moments." - CacheFly Team [21]
During high-demand events like product launches or live streams, cache shielding acts as a buffer, preventing the origin server from being overwhelmed [21]. To maximize its benefits, combine shielding with long TTL settings for static assets and versioned URLs (e.g., style.v2.css) [21][22]. Beyond performance, shielding also enhances security by mitigating DDoS attacks before they can impact your origin [21].
While shielding helps consolidate requests, further improvements can be achieved by efficiently distributing them through sharding.
Cache sharding splits cache storage across multiple servers within a single Point of Presence (PoP), reducing the load on any single server. Instead of relying on one cache server to handle all content for a location, sharding allocates different types of content or requests across multiple servers based on factors like content type, geography, or traffic patterns [21].
When memory limits lead to frequent cache evictions, scaling out by adding more nodes can help maintain performance [23]. Using consistent hashing minimizes the need to repopulate the cache when new nodes are introduced [23]. To avoid a "thundering herd" of cache misses when a new node goes live, prewarm it by preloading frequently requested data using scripts [23].
For further efficiency, a hybrid caching model can be adopted, where less critical data is stored on SSDs to reduce DRAM usage while maintaining low latency.
High eviction rates often signal low cache hit rates and the need for additional shards. Combining Least Frequently Used (LFU) policies with TTL expirations ensures that relevant data is retained while outdated content is purged [5].
Once your caching methods are fine-tuned, it’s essential to monitor their performance to address any emerging issues.
Real-time analytics tools are invaluable for identifying why content bypasses the cache and reaches your origin server. By filtering traffic based on status codes (HIT, MISS, EXPIRED, REVALIDATED, DYNAMIC), you can quickly pinpoint bottlenecks [24][6]. Analyzing the top URLs that generate cache misses helps focus optimization efforts on high-demand assets [24].
For a well-optimized site, the cache hit ratio for static assets should exceed 90% [3]. If analytics reveal a high "Dynamic" status for HTML files, consider implementing specific cache rules to enable caching [6]. Frequent "Expired" or "Revalidated" statuses suggest the need to increase Edge Cache TTLs using Cache-Control headers [6][22].
Pay close attention to request metrics, as every cache miss adds latency. Tools like curl can help debug requests in real time by using diagnostic headers such as X-Cache and X-Cache-Status [3]. Additionally, analytics can uncover cache key fragmentation, which occurs when unnecessary query strings, cookies, or headers create multiple unique cache keys for identical resources [2][22]. To address this, normalize variations (e.g., ?a=1&b=2 vs. ?b=2&a=1) using edge functions to consolidate cache entries [2][22].
SurferCloud's CDN operates across more than 17 availability zones spread over 4 continents, designed to cut down latency and reduce the load on origin servers. This global setup is built to maintain a 99.95% availability rate, thanks to redundant systems and kernel hot patch technology, which applies security updates without needing server reboots[25]. Its intelligent routing system ensures requests are sent to the nearest edge server, adapting to real-time network conditions. Plus, an easy-to-use dashboard allows for detailed control of resource allocation and performance tracking. For businesses managing static assets like images, CSS, and JavaScript files, SurferCloud can deliver cache hit ratios of over 90%[3].
SurferCloud’s infrastructure is designed to boost cache performance by reducing latency and ensuring reliable content delivery. With data centers strategically placed worldwide, users experience quick load times whether they're browsing from Tokyo or New York. The platform also supports various payment methods, making it accessible to users globally[25]. To top it off, their 24/7 expert support team is ready to resolve any cache-related issues, ensuring a seamless experience for both businesses and their customers.
To get started with SurferCloud, follow these steps:
These steps ensure a smooth implementation process and help maintain optimal cache efficiency for your site.
Getting the most out of your cache requires a mix of thoughtful setup and ongoing management. Effective practices include using aggressive Cache-Control headers with long time-to-live (TTL) values for static assets, cleaning up cache keys by removing unnecessary query parameters (like UTM tags), and adopting asset versioning to ensure files can be cached safely for longer periods. Infrastructure tweaks, such as Origin Shielding, add an extra cache layer to lighten the load on your origin server, while cache warming pre-loads edge servers before traffic spikes. Together, these approaches help maximize cache hit rates, which can lead to noticeable gains in site performance, reduced bounce rates, and higher conversions. These aren’t just quick fixes - they lay the groundwork for long-term efficiency.
The rewards of optimizing your cache go well beyond faster load times. Lower latency improves Time-to-First-Byte (TTFB), often delivering content in milliseconds rather than seconds, which can enhance search rankings and keep users engaged. This speed advantage can directly impact sales and retention by creating a smoother user experience. High cache hit ratios also cut costs by reducing bandwidth and egress fees - streaming giants like Netflix and Disney+ have managed to slash egress costs by up to 60% through smart caching strategies[4]. Beyond cost savings, edge caches add resilience during traffic surges and can even serve stale content during origin server outages, ensuring your site stays up when it matters most.
"Every percentage point gained in your cache-hit ratio is a competitive advantage - more speed, reduced costs, and happier users." - BlazingCDN[4]
By using these strategies, you can position your site for better performance and reliability.
Ready to take the next step? Start by exploring SurferCloud's CDN. With its global network of over 17 data centers and intelligent routing that adjusts to real-time conditions, it simplifies cache optimization. Begin by auditing your current Cache-Control settings and analyzing hit/miss metrics to identify areas for improvement. Quick wins often come from URL normalization and asset versioning, which can show results almost immediately. For businesses managing heavy traffic across multiple regions, consider advanced solutions like tiered caching or Origin Shielding. SurferCloud’s dashboard provides detailed insights into your cache performance, and their 24/7 support team is there to help troubleshoot any issues. Plus, their elastic scaling ensures your edge capacity expands automatically during traffic surges, keeping your cache performing smoothly when demand peaks. By maintaining strong cache hit ratios, you’ll enjoy faster load times, lower costs, and better outcomes for your business.
To figure out if your cache hit rate is where it should be, use this simple formula: divide the number of cache hits by the total cache requests (which is hits plus misses). Then, multiply that by 100 to get a percentage. A hit rate above 80% is typically seen as efficient for most websites.
If your hit rate is below this level, you might want to consider adjustments such as refining your caching rules, improving how content is delivered, or relying on a dependable cloud service to boost performance.
To boost your cache hit rate efficiently, try extending Edge TTLs to keep content cached for longer periods. Enable features like Origin Shield or tiered caching to cut down on repeated requests. Simplify and streamline URLs using custom cache keys, and fine-tune caching by including relevant query string parameters, cookies, or request headers - while removing unnecessary elements like Accept-Encoding. Serving static assets over HTTP can also speed up delivery.
These steps can help improve cache performance, delivering content faster and more reliably to your users.
Cache shielding, often referred to as Origin Shield, introduces an additional cache layer between the edge nodes and the origin server. This extra layer acts as a central hub, consolidating requests from various edge nodes. As a result, more content is delivered directly from the cache, reducing the need to repeatedly pull data from the origin server.
This approach helps lighten the load on the origin server, cuts down on latency, and boosts overall performance. It's a smart way to enhance cache efficiency while ensuring users enjoy a seamless experience.
? Pain Point Running chat relays between IRC, D...
When most VPS hosting plans start at $5–10 per month,...
When building and maintaining a website, selecting the ...